Say that we have a rogue access point in the vicinity. Using airodump-ng to capture packets, we get the following:

We can see that we have two networks with similar configurations, and the only changes we can see for now is the BSSID (MAC address) and the MB (link speed). While the MB is the most obvious change, let's investigate both MAC addresses at the MAC vendor's website, as follows:
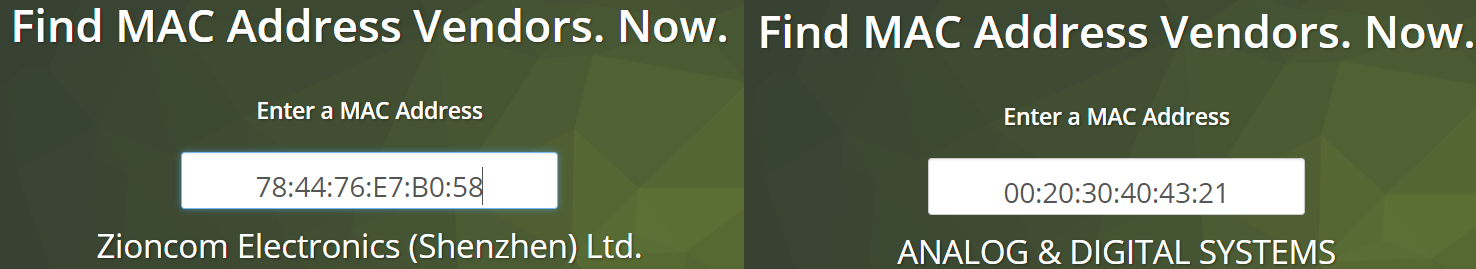
We can see that the address on the left is from Zioncom, which is a popular company that develops routers, while the address on the right is from a company called Analog & Digital Systems, which is not a router-manufacturing company. However, if the attacker has randomly spoofed this address, they could have done it for a legitimate-looking vendor. Additionally, we found an MB rate (maximum speed) that is missing an e from the airodump-ng result list. The missing e denotes whether the AP supports quality of service. The last thing we can denote from the airodump-ng interface is the speed at which beacons are transmitted. So, to sum up our first analysis, we have the following IoCs:
- Change in BSSID
- BSSID not resolving to a legitimate vendor (MAC vendors)
- Change in the data rate's quality of service parameter (a missing e means that QOS is not supported)
- An excessive number of beacon frames from the fake AP
While these are all key checks when it comes to a fake AP detection, we will certainly look for more.
