12
Consolidated Financial Statements
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
This chapter will help the readers to:
- Appreciate the rationale behind preparation of consolidated financial statements.
- Understand the basic principles and procedures in preparation of consolidated financial statements.
- Understand the concept of ‘minority interest’ in consolidated financial statements.
- Prepare consolidated financial statements.
- Get familiarity with the accounting and disclosure requirements under Ind AS 110 ‘Consolidated Financial Statements’ and Ind AS 28 ‘Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures’.
12.1 INTRODUCTION
A company having one or more subsidiaries is required to prepare a consolidated financial statement as per the provisions of the companies act 2013. For such companies, the annual report will have two sets of financial statements—one on a ‘standalone’ basis and the other on ‘consolidated’ basis. The need to present two set of accounts arises from the fact that these enterprises carry out a number of activities through their subsidiary companies. As the enterprise and its subsidiaries are separate entities, each of them prepares and presentsits financial statements on a standalone basis. Such financial statements reflect the results and financial position of each such entity individually. If one wants to understand the financial results of the group (consisting of the parent enterprise and its subsidiaries) or the assets and liabilities of the group, these individual statements are not very helpful. To better appreciate the financial performance of the group as a whole for the period and its assets and liabilities at the end of the accounting period, there is a need to consolidate all these standalone financial statements. Such consolidated financial statements will show the profit or loss of the group as a single entity, assets owned by the group as well as the liabilities it owes as a group. Ind AS 110 lays down principles and procedures for preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements.
Ind AS 110: These (consolidated) statements are prepared by combining the financial statements of all the group entities, with a view to determine the financial status of the group as if it was one single entity.
12.1.1 Scope of Consolidation
The users of financial statements are interested not only in the financial results of an enterprise but also of the group. The group for this purpose includes a parent company and its subsidiaries. The enterprise, being the parent company, needs to present its own financial statements on a standalone basis and also the financial statements of the group as a whole, aggregating the financials of the parent and its subsidiaries. The consolidated statements are in addition and not a substitute to the separate financial statements of the parent.
Ind AS 110: Group is a parent with all its subsidiaries. Parent is an entity that controls one or more subsidiaries. Subsidiary is an entity that is controlled by another entity.
For the purpose of consolidation, a parent is an enterprise that has one or more subsidiaries. All subsidiaries—both domestic and foreign—need to be consolidated with the parent to arrive at the group’s financial performance and position.
12.2 CONCEPT OF CONTROL
The parent–subsidiary relationship exists when the latter is controlled by the former. The obligation is upon the investor to determine whether it is a parent by assessing whether it controls the investee. An investor (parent) controls an investee (subsidiary) if all the following conditions are met:
- Investor has power over the investee.
- Investor is exposed to or has right to variable returns from the investee.
- Investor has the ability to use its power over the investee to affect the amount of the investor’s returns.
The conditions to be met to determine control of investor over investee are presented in Figure 12.1.

Figure 12.1 Concept of Control
12.2.1 Power
Power arises from rights—voting rights, contractual right, etc. An investor has power over an investee when the investor has existing rights that give it the current ability to direct the relevant activities. Relevant activities are activities that significantly affect the investee’s returns. Power arising from voting rights from shareholdings may be straightforward. Assessing power from other sources, e.g., contractual rights may be more complex.
12.2.2 Returns
If the returns to the investor have the potential to vary as a result of the investee’s performance, the investor is said to be exposed to variable returns from its involvement with the investee. The investor’s returns can be only positive, only negative or both positive and negative.
12.2.3 Link between Powers and Returns
An investor controls an investee if it also has the ability to use its power to affect the investor’s returns from its involvement with the investee.
12.3 CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As discussed earlier, the parent company in addition to its separate financial statements also needs to provide consolidated financial statements. The consolidated statements include:
- Consolidated statement of profit and loss
- Consolidated balance sheet
- Consolidated cash flow statement
- Explanatory notes and statements forming integral part of the above statements
These statements must be presented to the extent possible in the same format as used by the parent company for its separate statements. Consolidated financial statements are prepared using uniform accounting policies. If accounting policies followed by the different entities in the group are different from those used in the consolidated statements, suitable adjustments are required to be made in the financial statements while they are used for consolidation. Likewise, financial periods of the parent and subsidiaries used in the consolidated financial statements shall be the same. If the accounting period used by the subsidiary and parent is different, suitable adjustments need to be made for the effects of significant transactions and events that occur between the reporting dates of subsidiary and parent. The difference in reporting dates cannot be more than three months. If the gap is more than three months, the subsidiary has to prepare full financial statements at the parent’s year-end date.
The consolidation of parent and subsidiary companies is done on a line to line basis. The similar items of income, expenses, assets and liabilities are added together to arrive at the consolidated figures. However, intra-group transactions and intra-groups balances need to be eliminated during consolidation so that the consolidated numbers represent the group as a single economic entity.
12.4 CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS
The consolidated statement of profit and loss depicts the performance of the group as a single economic entity. It is prepared by aggregating various incomes and expenses on a line to line basis. Similar items of incomes and expenses are added together. However, two important adjustments need to be made while consolidating—firstly, intra-group transactions like sales, expenses and dividends are eliminated and secondly, the share of non-controlling shareholders in the profit of the subsidiary needs to be deducted from the consolidated profit or loss to arrive at parent’s share in subsidiary’s profit.
12.4.1 Intra-group Transactions
It may be possible, some transactions affecting the income or expenses have taken place between different members of a group. An item of income of one group member will become an expense for the other. While consolidating these incomes and expenses, such intra-group transactions need to be eliminated. After this adjustment, incomes and expenses will represent only transactions that have taken place between the ‘group’ on the one hand and external entities (non-group) on the other.
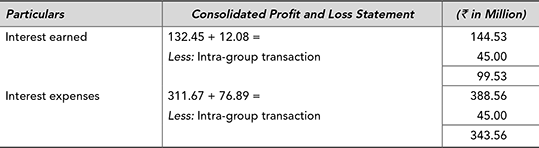
■ Illustration 12.1
The interest income and interest expenses of Fast Track Motors Limited and its subsidiary company Fast Track Components Limited for the year 2016–17 are given as follows:

During the year Fast Track Component paid a sum of ₹ 45 million to Fast Track Motors Limited towards interest on the amount borrowed from the parent company. How will interest earned and interest expenses be shown in the consolidated profit and loss statement?
While preparing consolidated profit and loss statement, intra-day transaction will be eliminated as follows:
12.4.2 Non-Controlling Interest
In case of a wholly owned subsidiary (where 100% ownership is held by the parent), the entire consolidated profit belongs to the group. In such a case, the profit figure of parent and subsidiary company will be added together. However, if part ownership of the subsidiary which is being consolidated is with external shareholders (called non-controlling interest), the entire profit or loss of the subsidiary does not belong to the group. In such cases, non-controlling interest (NCI) in the profit or loss of the subsidiary company needs to be quantified and adjusted from the consolidated profit to arrive at the profit belonging to the group.
■ Illustration 12.2
Let us assume that the Fast Track Motors Limited has 60% ownership of Fast Track Components Limited, the balance 40% being held by minority shareholders. The net profit earned by the two companies for the year amounted to ₹ 408.44 million and ₹ 132.65 million, respectively. Ascertain the consolidated profit.
The profit figures of the two companies will be added together and then adjusted for the minority interest as follows:
| (₹ in Million) | |
| Consolidated Profit ( ₹ 408.44 + ₹ 132.65) | 541.09 |
| Less: Minority Interest (40% of ₹ 132.65) | 53.06 |
| Profit after Minority Interest | 448.03 |
The net profit of ₹ 448.03 million represents the profit attributable to the owners of the parent company.
12.5 CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
While preparing the consolidated balance sheet, various items of assets and liabilities are added on a line to line basis. The consolidated balance sheet so prepared, shows the economic resources controlled by the group and the obligations of the group. However, certain adjustments relating to intra-group balances and non-controlling interest in the net assets of the consolidated subsidiaries need to be made. These adjustments are discussed in detail.
12.5.1 Cost of Investment
By investing in the shares of a subsidiary, the parent acquires a proportionate share in the equity of the subsidiary. The amount invested by the parent, appears as an investment on the assets side in its separate balance sheet. In the subsidiary’s balance sheet, the amount of equity appears on the liability side of the balance sheet. Equity for this purpose means the net assets of the subsidiary after deducting all its liabilities. The following situations are possible:
- The cost of investment made by the parent is exactly equal to parent’s portion in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investments. In this case, in the consolidated balance sheet, the investment made and parent’s portion in the equity of the subsidiary will exactly offset each other and will be eliminated.
- The cost of investment made by the parent is more than parent’s portion in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investments. In this case, in the consolidated balance sheet, the investment made and parent’s portion in the equity of the subsidiary will be eliminated and the excess will be recorded as goodwill on the asset side.
Goodwill: Excess of the cost of investment made by the parent over the parent’s share in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investment.
- The cost of investment made by the parent is less than parent’s portion in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investments. In this case, in the consolidated balance sheet, the investment made and parent’s portion in the equity of the subsidiary will be eliminated and the difference will be recorded as capital reserve on the liabilities side.
Capital Reserve: Excess of the parent’s share in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investment over the cost of investment made by the parent.
■ Illustration 12.3
Bright Gold Limited has three subsidiary companies. Based upon the information given in the following, ascertain how will the cost of investment be treated in the consolidated balance sheet.

The amount of goodwill or capital reserve will be calculated as follows:

The cost of investment made by Bright Gold Limited and its proportionate share in the equity (net asset) of the subsidiary companies will be eliminated from the consolidated balance sheet. In respect of its investment in the Hira Limited ₹ 18.98 million will be recognized as capital reserve in the consolidated balance sheet, whereas in respect of Sona Limited goodwill amounting to ₹ 34.34 million will be recorded in the consolidated balance sheet. No goodwill or capital reserve will be recognized in respect of investments made in Panna Limited as the cost of investments is exactly offsetting the parent’s share in the net assets of the subsidiary.
12.5.2 Non-Controlling Interest
In case of a wholly owned subsidiary (where 100% ownership is held by the parent) the entire equity of the subsidiary belongs to the group. In such a case, the equity of parent and subsidiary company can be added together on a line to line basis for the purposes of consolidation. However, if part ownership of the subsidiary which is being consolidated is with external shareholders (non-controlling interest), the entire equity of the subsidiary does not belong to the group. In such cases, non-controlling interest in the equity of subsidiary company needs to be quantified and shown in consolidated balance sheet separately from liabilities and the equity of the parent’s shareholders.
IND AS 110: Non-Controlling Interest—Equity in a subsidiary not attributable, directly or indirectly, to a parent.
While consolidating the balance sheet, the equity of the subsidiary is broken onto three parts:
- Non-controlling interest
- Parent’s share in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investment
- Parent’s share in the equity of the subsidiary after the date of investment
The non-controlling interest (1 above) is shown separately in the consolidated balance sheet. Parent’s share in the equity of the subsidiary at the time of making the investment (2 above) is offset against the cost of investment and is eliminated from the consolidated balance sheet. The parent’s share in the equity of the subsidiary after the date of investment (3 above) is aggregated in the consolidated balance sheet.
12.5.3 Intra-group Balances
While preparing the consolidated balance sheet, intra-group balances are identified and eliminated. For example, if the parent company has lent money to the subsidiary company, the same will be appearing on the asset side of parent company as loans and advances and on the liability side of the balance sheet of the subsidiary company as borrowed funds. In the consolidated balance sheet, both these balances will be eliminated to present the group as one economic unit.
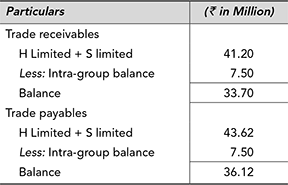
■ Illustration 12.4
On the basis of the separate balance sheets of H Limited and S Limited and additional information, prepare the consolidated balance sheet as on 31st December 2017:

Additional Information
- H Limited acquired 70% equity share of S Limited on 1st April 2016.
- At the time of making the investments, the other equity balance in the books of S Limited stood at ₹ 250 million.
Working
Capital Reserves

Non-Controlling Interest
30% of equity as on 31st March 2017 = 30% of ₹ 630 million = ₹ 189 million
Other Equity
Addition to other equity of S Limited since acquisition = ₹ 430 million – ₹ 250 million = ₹ 180 million
70% of increase in other equity H’s share = ₹ 180 million × 70% = ₹ 126 million.
Consolidated other equity = ₹ 1,890 million + ₹ 126 million = ₹ 2,016 million.
Intra-group Balances
Loan to S Limited in H Limited balance sheet will be offset against the borrowed funds in the balance sheet of S Limited. Borrowed funds in the consolidated balance sheet will be equal to ₹ 3,250 + ₹ 640 – ₹ 420 = ₹ 3,470 million. Loan to S Limited will not appear in the consolidated balance sheet.
Consolidated Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2017

12.5.4 Unrealized Profit on Intra-group Transactions
As discussed in the earlier paragraphs, intra-group transactions and balances are eliminated in full. Some of these intra-group transactions may result in unrealized gain or losses which are included in the balance amount of assets, e.g., inventory or fixed asset. Such unrealized profits or losses are identified and eliminated from the consolidated profit and loss statement as well as balance sheet.
■ Illustration 12.5
S Limited is a subsidiary of H Limited which own 60% of the equity shares of S Limited. During the year 2016–17, S Limited sold goods costing ₹ 120 million to H Limited for ₹ 180 million. Out of these, 1/3 of goods are still in stock of H Limited on the date of the balance sheet. How will the above transaction be consolidated?
Sale of ₹ 180 million by S Limited has been recorded as purchase by H Limited for the same amount. Both these transactions will be eliminated from the consolidated profit and loss statement. S Limited sold these goods a margin of 50% on cost recognizing a profit of ₹ 60 million. As 1/3rd of the goods are still in stock of H Limited, 1/3rd of these profits, i.e., ₹ 20 million, are unrealized. Out of these unrealized profits, 60%, i.e., ₹ 12 million, belongs to the group and needs to be eliminated. In the consolidated profit and loss statement, a deduction of ₹ 12 million will be made towards unrealized profit. The amount of inventories in the consolidated balance sheet will also be reduced by the same amount.
12.6 INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES AND JOINT VENTURES
Ind AS 28 defines an associate as an entity over which the investor has significant influence. The power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of the investee is indication of significant influence. Control or joint control over these policies is not a requisite condition for being an associate. In case of a joint venture, parties have joint control over the investee. Decisions about the relevant activities require the unanimous consent of the parties sharing control. The parties having joint control also have rights to the net assets of the arrangement.
12.6.1 Initial Measurement
Investment in an associate or a joint venture should be accounted using the equity method. Investment is initially recognized at cost, i.e., purchase price and any directly attributable expenditures necessary to acquire that investment. The difference between the cost of investment and entity’s share of the net fair value of the investee’s identifiable assets and liabilities is accounted either as goodwill or capital reserve.
If the cost of investment is greater than the entity’s shares of net fair value of the investee’s identifiable assets and liabilities, the difference in recorded as goodwill. If, however, the entity’s share of net fair value of the investee’s identifiable assets and liabilities is greater than the cost of investment, the difference is recorded as capital reserve.
12.6.2 Subsequent Measurement
The investment in an associate or joint venture is to be tested for impairment as single asset by comparing its recoverable amount with its carrying amount, if there are impairment indicators. Goodwill so recognized is not eligible for amortization and is not tested for impairment separately. The consolidated statement of profit and loss would include the Group’s share of profit or loss and other comprehensive income.
Box 12.1 Accounting policy of Biocon Limited Regarding Basis of Consolidation.
Subsidiaries
Subsidiaries are entities controlled by the Group. The Group controls an entity when it is exposed to, or has rights to, variable returns from its involvement with the entity and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the entity. The financial statements of subsidiaries are included in the consolidated financial statements from the date on which control commences until the date on which control ceases.
The financial statements of the Group are consolidated on line-by-line basis. Intra-group transactions, balances and any unrealized gains arising from intra-group transactions are eliminated. Unrealised losses are eliminated, but only to the extent that there is no evidence of impairment. All temporary differences that arise from the elimination of profits and losses resulting from intragroup transactions are recognized as per Ind AS 12, Income Taxes.
For the purpose of preparing these consolidated financial statements, the accounting policies of subsidiaries have been changed where necessary to align them with the policies adopted by the Company.
Annual report of Biocon Limited for the year 2016–17
Biocon Limited presented consolidated financial statements in its annual report for the year 2016–17 by consolidating the financials of 10 subsidiary companies and one joint venture. The accounting policy of the company relating to consolidation principles is given in Box 12.1.
Non-controlling Interests (NCI)
NCI are measured at their proportionate share of the acquiree’s net identifiable assets at the date of acquisition.
Changes in the Group’s equity interest in a subsidiary that do not result in a loss of control are accounted for as equity transactions.
Loss of Control
When the Group loses control over a subsidiary, it derecognizes the assets and liabilities of the subsidiary, and any related NCI and other components of equity. Any interest retained in the former subsidiary is measured at fair value at the date the control is lost. Any resulting gain or loss is recognized in statement of profit and loss.
Associates and Joint Arrangements (Equity Accounted Investees)
An associate is an entity in which the Group has significant influence, but not control or joint control, over the financial and operating policies. A joint venture is an arrangement in which the Group has joint control and has rights to the net assets of the arrangement rather than rights to its assets and obligations for its liabilities.
Interests in associates and joint ventures are accounted for using the equity method. They are initially recognized at cost which includes transaction costs. Subsequent to initial recognition, the consolidated financial statements include the Group’s share of profit or loss and OCI of equity-accounted investees until the date on which significant influence or joint control ceases.
Summary
- Consolidated financial statements are needed to understand the financial performance and position of a group.
- A group consists of a parent and its subsidiaries. An enterprise in which more than 50% voting power is held by another or its composition of board of directors is controlled by the other entity is called the subsidiary of the other enterprise (called parent).
- The parent needs to present consolidated financial statements in addition to its own separate financial statements.
- To the extent practical, while preparing the consolidated statements, the accounting policies used should be uniform and the financial statements used should be drawn up to the same reporting date.
- Consolidation is done by adding the financial statements of the parent and subsidiaries on a line-by-line basis. Intra-group transactions and intra-group balances are eliminated.
- The cost of investment made by the parent is set off against its proportionate share in the equity of the subsidiary. The difference between cost of investment and its share in equity, if positive, is recorded as goodwill and, if negative, is recorded as capital reserve in the consolidated balance sheet.
- Non-controlling interest in the net income of the subsidiaries is quantified and deducted from the combined profits. NCI in the net assets of the subsidiaries is identified and reported separately in the consolidated balance sheet.
- Interest in jointly controlled entities is reported in the consolidated financial statements using proportionate consolidation. In addition to subsidiary companies and joint ventures, financial statements of associates also need to be consolidated. An associate is an enterprise in which the investor has a significant influence and which is not a subsidiary or a joint venture of the investor.
Assignment Questions
- What is the purpose behind preparation of consolidated financial statements?
- How do we define the expression ‘group’ for the purpose of consolidation?
- ‘Intra-group transactions and intra-group transactions need be eliminated while consolidating’. Explain the statement with suitable examples.
- How is the cost of investment in the subsidiary company treated?
- Define the expression ‘minority interest’. How is minority interest disclosed in the consolidated financial statements?
Problems
- Goodwill or capital reserve on consolidation: Big Bull Limited acquired 70% of equity shares of Small Cow Limited for a total consideration of ₹ 435.45 million. At the time of acquisition the equity share capital of Small Cow Limited stood at 20 million equity shares of ₹ 10 each and the other equity balance at ₹ 320 million.
- Compute the amount at which the goodwill or capital reserve will be recognized in the consolidated balance sheet.
- What will be the goodwill or capital reserve if the consideration was ₹ 235.45 million?
- How will the investment appear in the consolidated balance sheet in the above two situations?
- Intra-group transactions: S Limited, a 100% subsidiary company of H Limited, sold goods costing ₹ 120 million to H Limited for ₹ 160 million during the year. Out of these, 40% of the goods are still unsold and are included in the balance sheet of H Limited at cost to it. How will the above transaction be treated in the consolidated financial statements?
- Preparing consolidated balance sheet: From the following balance sheets of H Limited and S Limited and additional information prepare the consolidated balance sheet of H Limited.

Additional Information
- The face value of shares of both companies is ₹ 10.
- H Limited holds 60% share in S Limited at a cost of ₹ 78.52 million.
- At the time of acquisition, the other equity of S Limited stood at ₹ 9.60 million.
- Trade payables of S Limited includes a sum of ₹ 7.5 million due to H Limited.
- Preparing consolidated balance sheet: Hero Limited acquired the entire equity share capital of Zero Limited on 1st January 2017 for a consideration of ₹ 600 million. At the time of acquisition the share capital of Zero Limited consisted on 20 million equity shares of ₹ 10 each. The company had other equity amounting to ₹ 560 million.
The balance sheets of the two companies as on 31st March 2017, are given below:


Additional Information
- Zero Limited borrowed ₹ 1,000 million from Hero Limited on 1st January 2011 at 10% per annum. The loan amount and interest thereon is due to be paid.
- Hero Limited bought goods from Zero Limited for ₹ 200 million during the year. Zero Limited charged a margin of 25% on cost. Out of these goods, 1/4th are still unsold.
- The debtors for Zero Limited include an amount of ₹ 140 million receivable from Hero Limited.
Solutions to Problems
-
-

- As the consideration of ₹ 235.45 million is less than the Big Bull Limited’s share in the equity of the Small Cow Limited, the difference, ₹ 128.55 million, will be recognized as capital reserve.
- In either case, the investment amount will not appear in the consolidated balance sheet.
-
- Elimination for intra-group transactions: The transaction is appearing as ‘sale’ in the books of S Limited and as ‘purchase’ in the books of H Limited at ₹ 160 million. While consolidating, both the legs of the transaction will be eliminated. Consequently, both income and expenses will come down by the same amount with no impact on profit.
Elimination of unrealized profit: The goods were sold by S Limited to H Limited at a profit of ₹ 40 million. Out of these goods 40% are still unsold resulting in an unrealized profit of ₹ 16 million (40% of ₹ 40 million). The carrying cost of inventory in the consolidated balance sheet will be reduced by ₹ 16 million and at the same time the consolidated profit will be reduced by the same amount.
- Capital reserve

Minority interest

Other equity

Intra-group balances
Consolidated balance sheet

- The consolidated balance sheet as on 31st March 2017 is given as follows:

Working


Try It Yourself
- Goodwill or capital reserve on acquisition: The equity share capital of Black Pearl Limited as on 31st December 2017 stood at ₹ 250 million. The company has been in losses for the last few years and the accumulated losses in the balance sheet stood at ₹ 165 million. The promoters holding 60% stake in the company are not very hopeful about the future prospects of the company and decided to sell their entire stake to White Gold Limited for ₹ 45 million.
- Ascertain the amount at which goodwill or capital reserve will be recognized on consolidation.
- What will be the goodwill or capital reserve if the consideration is at ₹ 60 million?
- Intra-group transactions: HR Limited holds 100% equity of SR Limited. At the year end, in addition to presenting their separate financial statements, HR Limited presents consolidated financial statements as well. During the year the following transaction took place between these two companies:
- HR Limited sold goods to SR Limited at an invoice price of ₹ 40 million. The cost of these goods to HR Limited was ₹ 25 million. At the end of the year goods with invoice price of ₹ 15 million are still unsold.
- The entire invoice price of ₹ 40 million is outstanding to be received on the date of the balance sheet.
- HR Limited gave a short term loan of ₹ 80 million to SR Limited. The loan was repaid by SR Limited during the year with interest amounting to ₹ 4 million.
How will the above transactions be treated in the consolidated financial statements?
- Preparation of consolidated balance sheet: Satya Limited acquired 80% of equity capital of Sundra Limited on 1st April 2016 for ₹ 575 million in an all-cash deal. The balance sheets of the two companies immediately before the transaction are given in the following:

You are required to prepare the consolidated balance sheet of Satya Limited immediately after acquisition.
- Preparation of consolidated financial statements: After one year of acquisition both the companies presented their respective balance sheets as on 31st March 2017 as follows:

Additional Information
- During the year Sundra Limited sold goods costing ₹ 660 million to Satya Limited for ₹ 800 million which in turn sold it to its customers for ₹ 920 million.
- The trade receivables of Sundra Limited include a sum of ₹ 430 million receivable from Satya Limited.
- Satya Limited gave a loan of ₹ 1,000 million to Sundra Limited on 1st October 2016 at 10%. The principal and interest thereon is outstanding on the date of the balance sheet.
You are required to prepare the consolidated balance sheet on 31st March 2017.
Cases
Case 12.1: Preparation of Consolidated Financial Statement: GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Limited1
Glaxo has a wholly owned subsidiary—Biddie Sawyer Limited (Biddie). Both the companies follow financial year as their accounting year. The summary of separate balance sheets of both the companies as on 31st December 2017 and the statement of profit and loss statement for the year ended on that date are given below:
Standalone Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2017


Standalone Statement of Profit and Loss for the Year Ended 31st March 2017


Additional Information
- The entire share capital of Biddie Sawyer Limited is held by GlaxoSmithKline Limited which was acquired at a cost of ₹ 4,761 lakh. The pre-acquisition reserves and surplus of Biddie stood at ₹ 4,665 lakh.
- The net receivables by Biddie from Glaxo from on the date of the balance sheet stood at ₹73 lakhs included in trade receivables of Biddie and other current financial liabilities of Glaxo.
- The revenue from operations of Glaxo include ₹24 lakhs earned from Biddie. The same amount has been included in other expenses of Biddie.
Based upon the above information, you are required to prepare the consolidated balance sheet for Glaxo Smith Kline Limited as on 31st December 2017 and the consolidated statement of profit and loss for the year ended 31st December 2017.
Case 12.2: Consolidated performance of Sun Pharmaceutical Limited2
Sun Pharmaceutical Limited is a leading pharmaceutical company of India engaged in research and manufacturing of drugs. It has over over 40 state-of-the-art manufacturing sites spanning 6 continents. These manufacturing units are located in India, the US, Brazil, Canada, Egypt, Hungary, Israel, Bangladesh, Mexico, Romania, Ireland, Morocco, Nigeria, South Africa and Malaysia. The company has around 2000 research scientists working in multiple R&D centres equipped with cutting-edge enabling technologies for research.
The company presents its financials both on standalone basis and on a consolidated basis. The consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31st March 2017 have been prepared taking into account the financials of the parent company and 134 subsidiary companies, partnership firms, joint venture and associate companies. The summarized financial statements of the company for the year ended 31st March 2017 are given below, both on standalone basis and on consolidated basis.
- Balance Sheet as on 31st March 2017:


- Statement of Profit and Loss for the Year Ended 31st March 2017


- Cash Flow Statement for the year ended 31st March 2017

Questions for Discussion
- To understand the financial performance and status of the Sun Pharmaceutical Limited, which of financial statements would you prefer?
- The company has reported a loss on standalone basis and profit on consolidated basis. What does it indicate?
- The expression ‘non-controlling interest’ is appearing in the profit and loss statement as well as in the balance sheet. What does it indicate?
- Why is goodwill appearing in the consolidated balance sheet but not in standalone balance sheet?
- ‘Investment in the nature of equity in subsidiaries’ is appearing the standalone balance sheet but not in the consolidated balance sheet. Why?
- Comment upon the cash flow under various activities on standalone basis as compared to consolidated basis.
Endnotes
- Based upon the Annual Report of Glaxo SmithKline Limited for the year 2017.
- Annual Report of Sun Pharmaceutical Limited for the year 2016–17.
