Reaction Schemes
A1 Starting Materials (Section 2.1)
- 3,3′- or 3,3′,5,5′-Substituted 4,4′-diaminodiphenyls (Section 2.1.1):

- Acetoacetic acid arylides (Section 2.1.2):

- 2-Naphthol, 2-hydroxy-3-naphthoic acid and Naphthol AS (Section 2.1.2.2):

A2 Synthesis of Hydrazone Pigments (Section 2.2)
- Diazotization (Section 2.2.1):
Preceding equilibria for the formation of XNO (XCl, Br, NO2, HSO4):

Diazotization (Ar: aromatic group):

Side reaction in the presence of an excess of −OH:

Decomposition (thermal):

- Coupling (RH = coupling component) (Section 2.2.2):

Side reaction in the case of acid deficiency (esp. with weak amines):

A3 Monohydrazone Yellow and Monohydrazone Orange Pigments (Section 2.3)
- Non-laked monohydrazone yellow and orange pigments:

- Monohydrazone yellow and orange pigment lakes (Section 2.3):

A4 Dihydrazone Pigments (Section 2.4)
- Diarylide yellow pigments (Section 2.4.1):

- Bisacetoacetarylide pigments (Section 2.4.2):

- Dihydrazonepyrazolone pigments (Section 2.4.3):

A5 ß-Naphthol Pigments (Section 2.5)

A6 Naphthol AS Pigments (Section 2.6)

A7 Red Hydrazone Pigment Lakes (Section 2.7)
- ß-Naphthol pigment lakes (Section 2.7.1):

- BONA pigment lakes (Section 2.7.2):

- Naphthol AS pigment lakes (Section 2.7.3):

- Naphthalene sulfonic acid pigment lakes (Section 2.7.4):
- Coupling in the 1-position:

- Coupling in the 7-position:

- Coupling in the 1-position:
A8 Benzimidazolone Pigments (Section 2.8)

A9 Dihydrazone Condensation Pigments (Section 2.9)
- Yellow pigments:
Type 1:

Type 2:

- Red pigments:

A10 Phthalocyanine Pigments (Section 3.1)
- Phthalonitrile process (Section 3.1.2.1):

- Phthalic anhydride/urea process (Section 3.1.2.2):

A11 Quinacridone Pigments (Section 3.2)
- Thermal ring closure (Section 3.2.1.1):

- Acidic ring closure (Section 3.2.1.2):

- Dihalo-terephthalic acid process (Section 3.2.1.3):

- Hydroquinone process (Section 3.2.1.4):

- Substituted quinacridone pigments (Section 3.2.1.5):

- Quinacridone quinone synthesis (Section 3.2.1.6):

A12 Perylene and Perinone Pigments (Section 3.4)
Naphthalene tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride:

A13 Diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) Pigments (Section 3.5)

A14 Indigo, Thioindigo and Thiazine Indigo Pigments (Section 3.6)
- Thioindigo Pigments (Section 3.6.2)
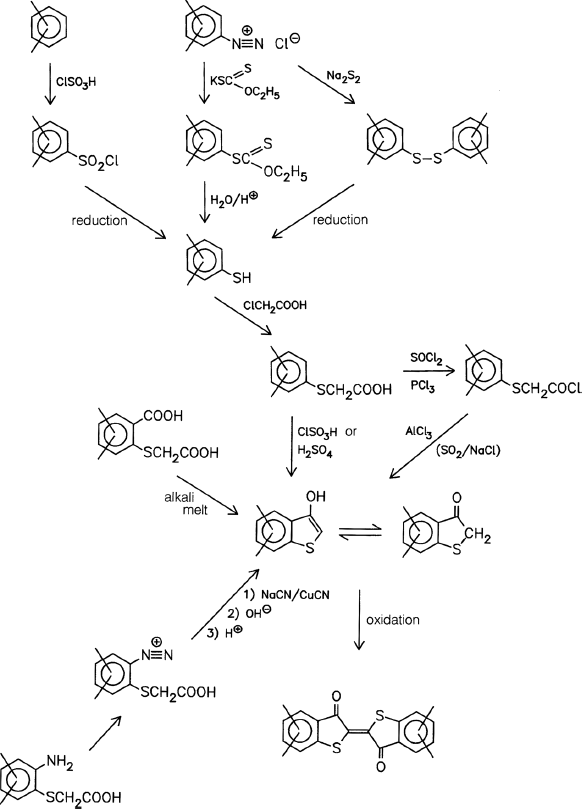
- Thiazine Indigo Pigments (Section 3.6.3)

A15 Various Polycyclic Pigments Derived from Anthraquinone (Section 3.7)
Heterocyclic Anthraquinone Pigments (Section 3.7.3)
- Anthrapyrimidine (Section 3.7.3.1):

- Indanthrone and Flavanthrone Pigments (Section 3.7.3.2):
Indanthrone:

Flavanthrone:

Polycarbocyclic Anthraquinone Pigments (Section 3.7.4)
- Pyranthrone pigments (Section 3.7.4.1):

- Anthanthrone pigments (Section 3.7.4.2):

- Isoviolanthrone pigments (Section 3.7.4.3):

- Violanthrone Pigments (Section 3.7.4.4):

A16 Dioxazine Pigments (Section 3.8)

A17 Quinophthalone Pigments (Section 3.9)

A18 Isoindolinone and Isoindoline Pigments (Section 3.10)
- Azomethine type: tetrachloroisoindolinone pigments:

Dainippon ink process:

- Methine type: isoindoline pigments:

A19 Triarylcarbonium Pigments (Section 4.1)
- Inner salts of sulfonic acids (Section 4.1.1):

- Dye salts with complex anions (Section 4.1.2):
Triphenylmethane and diphenylnaphthylmethane derivatives:

Replacing DMA in the above scheme by N,N-diethylaniline and 1-N,N-ethylnaphthylamine, resp., affords Victoria Blue types:

Phenylxanthene derivatives:

Benzothiazolium derivatives:

A20 Metal Complex Pigments (Section 4.2)
- Azo metal complexes (Section 4.2.1.1):
Pigment Green 10:

Complexes of azo-barbituric acid:

- Azomethine metal complexes (Section 4.2.1.2):
From aromatic o-hydroxy aldehydes:

From diimino-butyric acid anilides:

From isoindolinones:

