Transparency

The audit process begins by determining the scope of the audit—the organization, process, department, or system to be reviewed.
Next, the objectives of the audit are communicated. These include confirming accounting practices, streamlining processes, or improving system effectiveness.
Knowing the scope and objectives helps us hone in on the records needed as input for the audit. The audit must follow the rules set forth in laws, regulations, and company policies.
The auditors invest time in reviewing the records and meeting with support staff and other employees, in order to complete the audit. Once the audit is complete, the results are documented.
A blockchain application of this process will contain a ledger of all of the records by date, making the auditing process much more automated (rather than manually searching through digital files on multiple computers, or rummaging through paper documentation). Smart contracts can be used to proactively create timely auditing reports and email them to management, regulators, and auditors.
Auditing costs companies a fortune today. The average hourly fee for auditing services was over $150 in 2017.8
Blockchain can save organizations billions of dollars by storing relevant input data in the ledger and using smart contracts to automatically produce periodic reports.
A blockchain application of this process will require cooperation among organizations, auditors, and tax collectors.
Streamlining
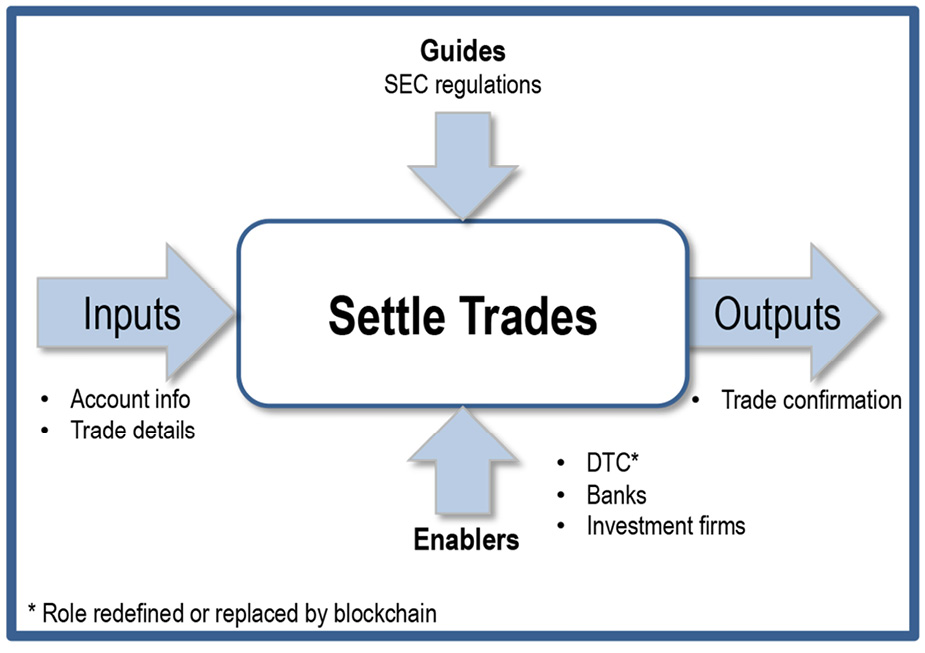
To settle a trade, we need the buyer’s or seller’s account information, plus the trade details. Banks, investment firms, and the Depository Trust Company (DTC) can all participate in settling a trade. When someone places an order for 100 shares of IBM stock, the trade confirmation is not received until the settlement process is complete.
The Depository Trust Company (DTC) is ultimately responsible for making sure the transaction is completed safely and securely.
The DTC acts as a clearinghouse to process and settle trades in corporate and municipal securities. In addition to safekeeping, recordkeeping, and clearing services, the DTC provides direct registration, underwriting, reorganization, and proxy and dividend services.9
It can take days for this trusted intermediary to validate the process, acting as a clearing agent. All communication with the DTC takes place through brokers, banks, and settlement agents—each also acting as intermediaries for related processes. I worked on Wall Street when we went from settling a trade in five days to three. It was a major accomplishment.
In 2014, settling a trade went from three days to two days, but that still is a lot of time. It is expensive, too; settling trades in the financial industry costs upwards of $80 billion a year globally.10
By using blockchain technology and removing or redefining the role of the DTC in the process, trades can take as little as ten minutes and cost pennies.
In addition, all of the details associated with trades are stored in the ledger, instead of using costly archival methods (including paper).
There is currently substantial effort being invested into building a blockchain application in this area, but success will require lots of cooperation among banks, investment firms, and the DTC.
Privacy

Insider trading is the buying or selling of a security by someone who has access to material, nonpublic information about the security. Insider trading can be illegal or legal, depending on when the insider makes the trade. It is illegal when the material information is still nonpublic.11 For example, if someone has news that will most likely make IBM stock skyrocket, and they buy the stock before this news is made public, that is illegal. However, if they announce the news, or wait until the news is announced before buying the stock, that is legal.
A blockchain application can be used to minimize insider trading. The person can easily post (or have someone post) the news via blockchain, and it remains anonymous, yet creates a permanent record of when the story was posted. The person can then immediately buy or sell the stock legally, as the trade will be made after the story was posted.
A challenge with posting news from anonymous sources is that it creates an incentive to spread “fake news,” which are false stories that appear to be factual news, spread on the internet or using other media.12 Imagine someone posting fake news about IBM and how that might impact the IBM stock price.
Permanence

When someone sells a stock, often there is a gain or loss that must be reported for tax purposes. A few years ago, I was switching brokerage firms and moving my stocks to the new firm. When I traded those stocks, I needed to report capital gains on my tax form. However, I bought the stocks so long ago that it took me hours to find the paper trade statements; I was glad that I still had them at all!
A blockchain trading system will record when every buy and sell transaction occurred. Furthermore, using a smart contract to initiate a capital gains summary of the trade would make the whole capital gains process automated. This would save people hours of time searching for statements, and reduce paper usage.
Distribution

Crowdfunding is a process of raising money for a project through lots of small investments from many people. There are intermediaries today that facilitate crowdfunding, such as Kickstarter and Indiegogo.
Blockchain allows companies to crowdfund without these intermediaries. Startups can create their own digital currency in blockchain; the currency is equivalent to shares in the company, which can be sold to investors.
Startups such as Swarm, Koinify, and Lighthouse have raised millions using this blockchain approach.13
