Chapter 3
Project Portfolio Management in Practices
The five organizations use different approaches to PPM. While some organizations have an independent entity for PPM, the others manage their portfolio as part of their business operations. Despite their different approaches, these organizations practice portfolio alignment and portfolio monitoring and control processes. Senior-level executives of these organizations are involved in the portfolio governance. All five organizations practice standardized project management processes and methodologies.
PPM Practices in Each Organization
Alpha is a communications services company serving the U.S. market with communications services for residential and business customers. In this study, we investigated the portfolio of network projects, which is managed under a network program management office (Network PMO) of the global shared-services (GSS) business group. The purpose of the Network PMO is to ensure the delivery of the network projects. In general, the project funding process starts with a capital planning process at the corporate level. Each business unit (BU) enters its initiatives as part of a capital request in the company's capital planning tool. After the investigation of the ROI at the corporate level and at each BU level, including the deliberated discussions and negotiations, funds are allocated to each BU.
In the network portfolio of GSS, the network projects are typically originated from marketing initiatives. During the preparation of a project for the selection and prioritization process, there are project sizing and costing activities that require collaboration between marketing and the network PMO. Based on the availability of funds, the executive committee (with support from marketing) selects projects based on projected revenue generation. The priority of the projects depends on the business priority and is set by the marketing team. The marketing team maintains a list of funded projects to be rolled out in a given year, including their priority, and makes the list available to the Network PMO. After being funded, the projects are planned and executed by the Network PMO.
As for project management, the Network PMO has a project management system that includes standardized project management processes and methodologies. The standard project management practices are followed depending on the type of project and there is information systems support to help with recording and reporting status and progress. During project execution, besides regular project status meetings, there is a monthly meeting to review the status of key projects with senior executives. The president and executives of GSS pay particular attention to the projects with the highest potential business impact and typically request a quarterly meeting with the project teams. Overall, Alpha has a mature strategic planning process. Through the executive committee, the project selection process, and the project governance by senior executives, the network portfolio had linkage to the overall business strategy.
Beta is an information services company serving the global insurance industry with statistical, actuarial, and claims-related products. At Beta, the project portfolio is managed under the project management office of the development division (Development PMO), established three-to-five years ago. The development division is aligned with businesses, having a manager and necessary resources for each unit. While there is no designated PPM office and staff, the Development PMO serves in this role. The portfolio consists of multiple development and infrastructure projects within the IT organization. The purpose of the PMO is to ensure the smooth utilization of resources, to alleviate resource contention issues, and to successfully manage high-priority projects in the portfolio. The PMO has a full-time PMO manager and seven project managers (direct reports). Other project managers reside within infrastructure and development organizations (indirect reports to the PMO manager). At any given time, there are approximately 30–40 projects in the portfolio.
Projects are typically initiated by the business during a budget cycle or an off cycle. Product managers (from the business units) and the PMO manager work collaboratively to develop requirements documents and the project charter. The project selection is conducted at the cross-business executive level. Major projects require approval from the CEO. This is accomplished annually as part of the capital budgeting process, providing funding for business operations. Once approved, the projects are listed in the portfolio dashboard and categorized and scored by the PMO manager. The project ranking is performed by the prioritization committee (BPC), consisting of four senior executives from the IT department. The rank of the project determines its priority when there is resource contention. The top 10 projects typically receive all the resources they need. The company has introduced tools and procedures that promote consistency in how the portfolio is prioritized and managed. For example, the PMO utilizes scoring sheets and systems to manage the ranking from the score sheets from each rater. Projects follow a toll gate process for project management, once approved. An online system was implemented and is used on a daily basis to ensure visibility into the projects and for tracking project status and issues. The system is available to all and supports transparency across the business and with management, according to the established hierarchy of permissions. There is an automatic notification if there are any conflicts or issues. The process is regarded as providing substantial improvement and benefit to the business. The PMO manager has a weekly meeting with project managers to discuss resource conflicts in the upcoming weeks. Another weekly meeting is also set to go over dashboard, milestones, and processes. Beta follows a strategic planning process. IT strategy was developed using top-down and bottom-up approaches. A strategic exercise is used to develop 10, 7, 3, and next-year visions and goals. These visions and goals are used as a foundation for the development of quarterly objectives and metrics.
Delta is an insurance company that has a dedicated corporate level project portfolio management office (PPMO), reporting to the vice president of strategy. The office has a dedicated director and staff. The PPMO is directly involved with the selection, prioritization, and governance of the corporate project portfolio through a prioritization committee (PC) and a project review committee (RC). The majority of approximately 40 projects in the portfolio were IT-related projects.
The PC is chaired by the director of the PPMO. The committee members are senior-level managers representing various functions, including businesses. The company's senior executives are not involved in making funding decisions, but they provide their perspective on the priority of projects related to the strategic direction of the company. Delta also has a benefit realization team (BT). This team is a result of a recent initiative to measure the realization of benefits from projects. The BT helps project teams identify benefits of their projects prior to presenting project proposals to the PC. The PC has sole authority in making project funding decisions and reports directly to the management committee, which consists of the company's senior executives. The PPMO maintains active oversight of the portfolio of projects through the RC, chaired by the director of PPMO. The RC emphasizes project delivery and provides inputs to the PC to make the go/kill decisions. For each project, funding decisions are made on a phase-by-phase basis. The quality process consultants, part of the IT excellence and quality organization, provide assistance to project managers to ensure project delivery. All corporate projects follow a standardized project management process that incorporates the interactions with the PC, RC, and BT. Delta has a mature strategic planning process. The organization has a company strategy map, including drivers and metrics. While the company's strategy does not change very often, it is revisited every 12–18 months and reviewed regularly.
Gamma is an international finance company that has a large portion of its projects involved with systems that support the firm's various financial transactions. The company has a dedicated PMO team that is part of the technology organization and reports into the CIO. The PMO is primarily concerned with project governance and facilitates monthly meetings with the CIO and the senior IT management team to review project status. Each project that meets the minimum criteria, as defined by the project steering committee, is reviewed on a monthly basis through a project summary report that is prepared by the project team. The PMO also manages compliance to the company's project life cycle and standardized documentation requirements, which is tracked via an online tool that can provide metrics and reporting around adherence to the processes.
The project portfolio is managed by a steering committee that consists of corporate-level executives, representatives of the various business units with the technology managers that directly support them, and members of the finance department. During the fourth quarter of each year, each business unit and its technology counterparts identify the large projects that seek to be initiated in the following year. A capital sheet template is completed for each of these proposed projects and includes project cost and benefit information. After the list of potential projects is reduced through preliminary discussions, it is presented to the steering committee, and a subset of the requests receives approval for funding in the following year. This selection committee meets on a quarterly basis to review the entire portfolio and make decisions as to whether the current set of projects should proceed or if there are any projects that need to cease. New “unplanned” projects may also request funding at these quarterly meetings.
After projects receive funding approval from the portfolio steering committee, there is a high-level planning meeting held with the CIO and the technology management team. This meeting provides visibility to the management team into upcoming projects that may require their resources. Also, those projects that receive approval to proceed are authorized to spend a subset of the funds granted for initial analysis. The next step is a review of the planned architecture to ensure it is consistent with corporate standards and that there is no redundancy. Once the project is ready to move to the next stage, it goes through one last review, led by the CIO and CFO, for authorization to spend the budgeted dollars. The project is then subject to the monthly project status review.
Lambda is a research and development center of the U.S. government. The organization is comprised of a large number of units, including engineering centers and enterprise offices. As a governmental center, Lambda receives funds from different sources, resulting in different categories of projects and different portfolios. The portfolio of emerging technology projects (ETP) was the focus of this study. There are approximately 40–50 projects in the portfolio. The ETP portfolio is championed by the director of science concept and technology (SC&T), who is a visionary and has a broad understanding of dependencies among technologies, including Lambda's strategy and war fighters’ interests. Without a dedicated office, the SC&T director is supported by staff from the business interface office and the project integration office.
The annual selection and evaluation of the ETP portfolio starts from requests for proposals. The proposals are then reviewed by the quality management board (QMB), consisting of representatives from engineering centers and enterprise offices. By keeping the strategy in mind, QMB evaluates proposals against the war fighter gaps, which has priority. This process is iterative, with extensive discussions between QMB and the proposal owner. After the evaluation, QMB proposes a list of projects to the SC&T director, who then makes the final selection. After funding, the projects are executed with the assistance of a project integrator (PI), who will contact the proposal owner and initiate the selection of a project manager. After the development of project preliminary documents (e.g., charter, preliminary plan, and acquisition strategy), the project funding is released by the SC&T director. The level of project (according to the category from the government) is decided and the project manager and the PI work on project execution. Project governance depends on the level of project.
Although Lambda's PPM process is more ad-hoc, it has standardized project management processes. The project integration office (PIO) owns the processes and facilitates the exercise of the processes and procedures through the PIs, who directly provide assistance to project managers. The PIO has 10 PIs and assistant PIs, dedicated to different programs. The PIO also provides project management training. Additionally, the PIO facilitates project performance reviews, which are conducted at different levels of rigor, depending on the level of project. Financial reviews are conducted through a fiscal-year budgeting process.
Similarities and Differences in PPM Practices
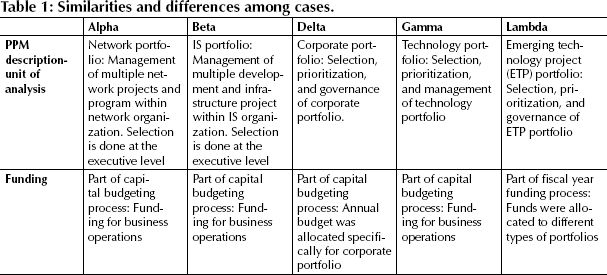
From the analysis, these five organizations used different approaches to PPM (see Table 1). While Delta has an independent entity and the most mature process for PPM, the others managed their portfolio as part of their business operations with the utilization of the project management office. At the corporate level, all four for-profit organizations followed their capital budgeting process to allocate funds across businesses. As a government center, Lambda receives different categories of funds from the government that they have to utilize within the scope of the prescribed execution policy.
For Alpha's network project portfolio, the project selection and prioritization were done by the businesses as part of the usual business operations. For Beta's development project portfolio, the project selection was performed by businesses, while the prioritization was done by the IT organization to ensure the appropriate allocation of IT resources. For Gamma, the technology projects were proposed by each business unit and its technology counterpart. After the initial vetting process, the projects were selected by a selection committee. Different from the other companies, Delta allocated a discretionary budget to its corporate project portfolio and utilized an independent portfolio prioritization committee, operating separately from the company's business units. In Lambda's case, the center receives funding for its ETP portfolio. The center utilizes a committee to evaluate the proposals. No matter what approaches the companies used, projects in their portfolio were selected to support the organization's strategic directions and operations. Since revenue generation was important for Alpha, the projects were selected based on the revenue they were expected to generate. Beta's portfolio also supported its businesses. Delta utilized a benefit realization committee to unsure that the project benefits were articulated. The projects were selected and prioritized based on their benefits and their alignment with the company's strategic direction. Gamma emphasizes return on investment, operational improvement, and regulatory compliance during project selection. Lambda puts more attention to war fighters’ gaps during the selection process.




As for project management, all five organizations practice standardized project management processes and methodologies. They utilize project management offices to help ensure the successful delivery of the projects in the portfolio. For Alpha, based on the types of products or services generated by projects, the network projects were assigned to the relevant group under the network PMO. Each group had its own project managers who were the direct reports of the group director. Beta utilized a centralized development PMO for managing development projects. Project managers are the direct reports of the PMO manager. Since Delta's corporate projects involve IT elements, the projects were managed under the IT organization in which the IT excellence and quality group provided project management consultants to project managers to ensure successful project delivery. Gamma has an enterprise PMO to promote standardized project management processes and facilitate project management governance. It also has divisional PMOs that support its businesses. Lambda utilizes a project integration office to promote standardized project management processes and to provide assistance to the project managers.
In all five organizations, senior-level executives were involved in the portfolio governance. Alpha's executives paid significant attention on the network portfolio, especially the strategic initiatives. Beta's CIO and vice presidents were informed about the status of projects in the portfolio through its PMO. Delta's executives received the status of the portfolio through the director of the corporate project portfolio, on behalf of the portfolio prioritization committee. Gamma's CIO and senior executives are members of the portfolio steering committee. Lambda's senior personnel participate in proposal selection and project governance.
Despite their different approaches to PPM, all five organizations practiced portfolio alignment and portfolio monitoring and control processes. To different degrees, these organizations employed well-defined procedures, including formal and explicit methods for project portfolio management. Even though these organizations did not employ a specific measurement to assess the portfolio success, they emphasized the success of an individual project in the portfolio. Middle managers, such as portfolio managers and PMO managers, also play major roles in PPM. All five organizations continuously learn and implement new practices to improve their PPM.
