Chapter 3
Working with Voice and Accessibility

Your iPad includes the Siri personal assistant, helpful accessibility features, and integration with your Mac.
Gather and Share Information with Siri
Configure Siri to Work Your Way
Using VoiceOver to Identify Items On-Screen
Give Commands with Siri
The powerful Siri feature on your iPad enables you to take essential actions by using your voice to tell your iPad what you want. Siri requires an Internet connection, because the speech recognition runs on servers in Apple’s data center.
You can use Siri either with the iPad’s built-in microphone or with a headset microphone. You can get good results from the built-in microphone if you are in a quiet environment and you speak loudly and clearly, or if you can speak as close to the built-in microphone as possible. Otherwise, use a headset microphone, which will usually provide better results.
Open Siri

From the Home screen or any app, press the Home button or the headset clicker button — if the headset has one — for several seconds.
The Siri screen appears, showing the “What can I help you with?” prompt. Siri also plays a tone to indicate that it is ready to take your commands.
When your iPad is connected to a power source, you can also activate Siri by saying “Hey Siri” if the Allow “Hey Siri” feature is turned on in Settings.
Send an E-Mail Message

Say “E-mail” and the contact’s name, followed by the message. Siri creates an e-mail message to the contact and enters the text. Review the message, and then tap Send to send it.
You can also say “E-mail” and the contact’s name and have Siri prompt you for the various parts of the message. This approach gives you more time to collect your thoughts.
If your Contacts list has multiple e-mail addresses for the contact, Siri prompts you to choose the address to use.
Set an Alarm

Say “Set an alarm for 5AM” and check the alarm that Siri displays.
You can turn the alarm off by tapping its switch (![]() changes to
changes to ![]() ).
).
Send a Text Message

Say “Tell” or “Text” and the contact’s name. When Siri responds, say the message you want to send. For example, say “Tell Kelly Wilson” and then “I am stuck in traffic, but I’ll be there in an hour.” Siri creates a text message to the contact, enters the text, and sends the message when you say “Send” or tap Send.
You can also say “Tell” and the contact’s name followed immediately by the message. For example, “Tell Bill Sykes the package will arrive at 10AM.”
Set a Reminder for Yourself

Say “Remind me” and the details of what you want Siri to remind you of. For example, say “Remind me to take the wireless transmitter to work tomorrow morning.” Siri listens to what you say and creates a reminder. Check what Siri has written; if the reminder is correct, you need do nothing more, but if it is incorrect, tap Remove to remove it.
Set Up a Meeting
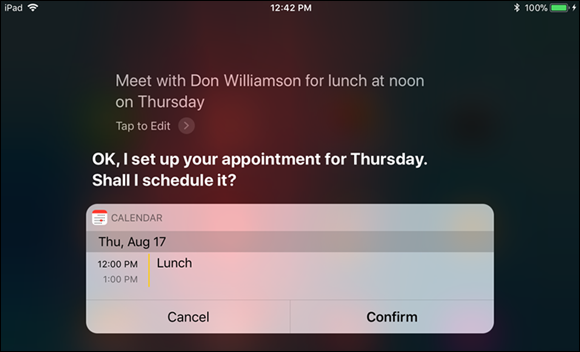
Say “Meet with” and the contact’s name, followed by brief details of the appointment. For example, say “Meet with Don Williamson for lunch at noon on Thursday.” Siri listens and warns you of any scheduling conflict. Siri then displays the appointment for you to check.
If you tap Confirm, Siri sends a meeting invitation to the contact if it finds an e-mail address. Siri adds the meeting to your calendar.
Dictate Text Using Siri
One of Siri’s strongest features is its capability to transcribe your speech quickly and accurately into correctly spelled and punctuated text. Using your iPad, you can dictate into any app whose keyboard displays the microphone icon (![]() ), so you can dictate e-mail messages, notes, documents, and more. To dictate, simply tap the microphone icon (
), so you can dictate e-mail messages, notes, documents, and more. To dictate, simply tap the microphone icon (![]() ), speak after Siri beeps, and then tap Done.
), speak after Siri beeps, and then tap Done.
To get the most out of dictation, it is helpful to know the standard terms for dictating punctuation, capitalization, symbols, layout, and formatting.
Insert Punctuation

To insert punctuation, use standard terms: “comma,” “period” (or “full stop”), “semicolon,” “colon,” “exclamation point” (or “exclamation mark”), “question mark,” “hyphen,” “dash” (for a short dash, –), or “em dash” (for a long dash, —).
You can also say “asterisk” (*), “ampersand” (&), “open parenthesis” and “close parenthesis,” “open bracket” and “close bracket,” and “underscore” (_).
For example, say “buy eggs comma bread comma and cheese semicolon and maybe some milk period nothing else exclamation point” to enter the text shown here.
Insert Standard Symbols

To insert symbols, use these terms: “at sign” (@), “percent sign” (%), “greater-than sign” (>) and “less-than sign” (<), “forward slash” (/) and “backslash” (), “registered sign” (®), and “copyright sign” (©).
For example, say “fifty percent forward slash two greater than ninety-seven percent forward slash three” to enter the computation shown here.
Insert Currency Symbols

To insert currency symbols, say the currency name and “sign.” For example, say “dollar sign” to insert $, “cent sign” to insert ¢, “euro sign” to insert €, “pound sterling sign” to insert £, and “yen sign” to insert ¥.
For example, say “the cost is dollar sign six or euro sign five per person” to enter the text shown here.
Control Layout

You can control layout by creating new lines and new paragraphs as needed. A new paragraph enters two line breaks, creating a blank line between paragraphs.
To create a new line, say “new line.” To create a new paragraph, say “new paragraph.”
For example, say “dear Anna comma new paragraph thank you for the parrot period new paragraph it’s the most unusual gift I have ever had period” to enter the text shown here.
Control Capitalization

You can apply capitalization to the first letter of a word or to a whole word. You can also switch capitalization off temporarily to force lowercase:
Say “cap” to capitalize the first letter of the next word.
Say “caps on” to capitalize all the words until you say “caps off.”
Say “no caps” to prevent automatic capitalization of the next word — for example, “no caps Monday” produces “monday” instead of “Monday.”
Say “no caps on” to force lowercase of all words until you say “no caps off.”
For example, say “give the cap head cap dining cap table a no caps french polish period” to enter the text shown here.
Insert Quotes and Emoticons

To insert double quotes, say “open quotes” and “close quotes.” To insert single quotes, say “open single quotes” and “close single quotes.”
To enter standard emoticons, say “smiley face,” “frown face,” and “wink face.”
For example, say “she said comma open quotes I want to go to Paris next summer exclamation point close quotes” to enter the text shown here.
Gather and Share Information with Siri
You can use Siri to research a wide variety of information online — everything from sports and movies to restaurants worth visiting or worth avoiding. You can also use Siri to perform hands-free calculations.
When you need to share information quickly and easily, you can turn to Siri. By giving the right commands, you can quickly change your Facebook status or post on your wall. Similarly, you can send tweets using your Twitter account.
Find Information About Sports

Launch Siri and ask a question about sports. For example:
“Siri, when’s the next Patriots game?”
“Did the Lakers win their last game?”
“When’s the end of the NBA season?”
“Can you show me the roster for the Maple Leafs?”
Find Information About Movies

Launch Siri and ask a question about movies. For example:
“How good is the movie Hell or High Water?”
“Siri, where is the movie Let’s Be Evil playing in Indianapolis?”
“What’s the name of Jason Statham’s latest movie?”
“Who’s the star of Nine Lives?”
Find a Restaurant

Launch Siri, and then tell Siri what type of restaurant you want. For example:
“Where’s the best Mexican food in Spokane?”
“Where can I get sushi in Albuquerque?”
“Is there a brewpub in Minneapolis?”
Address a Query to the Wolfram Alpha Computational Knowledge Engine

Launch Siri, and then say “Wolfram” and your question. For example:
“Wolfram, what is the cube of 27?”
“Wolfram, minus 20 Centigrade in Kelvin.”
“Wolfram, tangent of 60 degrees.”
“Wolfram, give me the chemical formula of formaldehyde.”
Find Out What Music You Are Listening To

Launch Siri and ask a question such as “What song is this?” or “Do you know what this music is called?” Siri monitors the microphone’s input, consults the Shazam music-recognition service, and returns a result if there is a match.
Translate to Another Language

Launch Siri, and then say “Translate to” and the name of the language, such as “Translate to Spanish.” When Siri prompts you for the text, speak it. Siri announces the translated text and displays it on-screen, together with a Play button (![]() ) that you can tap to play the audio again.
) that you can tap to play the audio again.
Configure Siri to Work Your Way
To get the most out of Siri, spend a few minutes configuring it. You can set the language Siri uses, choose between using a female voice and a male voice, and control when Siri should give you voice feedback. You can also enable or disable the “Hey Siri” feature, use Siri via the on-screen keyboard, or temporarily turn Siri off.
Most important, you can tell Siri which contact record contains your information, so that Siri knows your name, address, phone numbers, e-mail address, and other essential information.
Configure Siri to Work Your Way

![]() Press Home.
Press Home.
The Home screen appears.
![]() Tap Settings (
Tap Settings (![]() ). The Settings screen appears.
). The Settings screen appears.
![]() Tap Siri & Search (
Tap Siri & Search (![]() ).
).
The Siri & Search screen appears.
![]() Set the Listen for “Hey Siri” switch to On (
Set the Listen for “Hey Siri” switch to On (![]() ) to activate Siri by saying “Hey, Siri!”
) to activate Siri by saying “Hey, Siri!”
![]() Set the Press Home for Siri switch to On (
Set the Press Home for Siri switch to On (![]() ) to be able to press Home to summon Siri.
) to be able to press Home to summon Siri.
![]() Set the Allow Siri When Locked switch to On (
Set the Allow Siri When Locked switch to On (![]() ) to use Siri from the lock screen.
) to use Siri from the lock screen.
![]() Tap Language.
Tap Language.

The Language screen appears.
![]() Tap the language you want to use.
Tap the language you want to use.
![]() Tap Siri & Search (
Tap Siri & Search (![]() ).
).
The Siri & Search screen appears again.
![]() Tap Siri Voice.
Tap Siri Voice.
Note: To use Siri via the keyboard, press Home, tap Settings (![]() ), tap General (
), tap General (![]() ), tap Accessibility, tap Siri, and then set the Type to Siri switch to On (
), tap Accessibility, tap Siri, and then set the Type to Siri switch to On (![]() ).
).

The Siri Voice screen appears.
![]() In the Accent box, tap the accent you want, such as American.
In the Accent box, tap the accent you want, such as American.
![]() In the Gender box, tap Male or Female.
In the Gender box, tap Male or Female.
![]() Tap Siri & Search (
Tap Siri & Search (![]() ).
).
The Siri & Search screen appears again.
![]() Tap Voice Feedback.
Tap Voice Feedback.

The Voice Feedback screen appears.
![]() Tap Always On, Control with Mute Setting, or Hands-Free Only to specify when you want to receive voice feedback from Siri.
Tap Always On, Control with Mute Setting, or Hands-Free Only to specify when you want to receive voice feedback from Siri.
![]() Tap Siri & Search (
Tap Siri & Search (![]() ).
).
The Siri & Search screen appears again.
![]() Tap My Info.
Tap My Info.
The Contacts dialog appears.
Note: To change which contacts appear in the Contacts dialog, tap Groups, select the groups to display, and then tap Done.
![]() Tap the contact record that contains your information.
Tap the contact record that contains your information.
The name appears on the My Info button.
Using VoiceOver to Identify Items On-Screen
If you have trouble identifying the iPad controls on-screen, you can use the VoiceOver feature to read them to you. VoiceOver changes the standard iPad finger gestures so that you tap to select the item whose name you want it to speak, double-tap to activate an item, and flick three fingers to scroll. VoiceOver can make your iPad easier to use. Your iPad also includes other accessibility features, which you can learn about in the next section.
Using VoiceOver to Identify Items On-Screen

![]() Press Home.
Press Home.
The Home screen appears.
![]() Tap Settings (
Tap Settings (![]() ).
).
The Settings screen appears.
![]() Tap General (
Tap General (![]() ).
).
The General screen appears.
![]() Tap Accessibility.
Tap Accessibility.
The Accessibility screen appears.
![]() Tap VoiceOver.
Tap VoiceOver.
Note: You cannot use VoiceOver and Zoom at the same time. If Zoom is on when you try to switch VoiceOver on, your iPad prompts you to choose which to use.
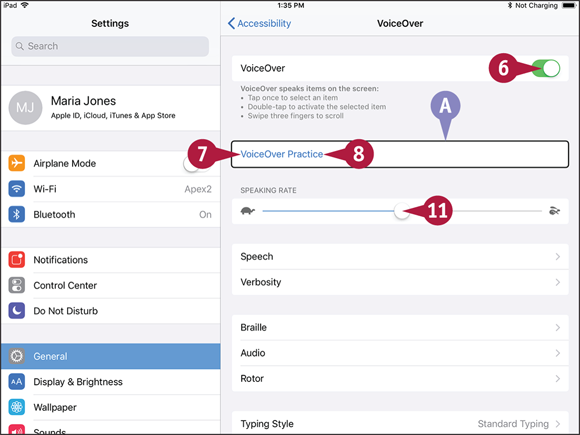
The VoiceOver screen appears.
![]() Set the VoiceOver switch to On (
Set the VoiceOver switch to On (![]() ).
).
![]() Tap VoiceOver Practice.
Tap VoiceOver Practice.
![]() A selection border appears around the button, and VoiceOver speaks its name.
A selection border appears around the button, and VoiceOver speaks its name.
![]() Double-tap VoiceOver Practice.
Double-tap VoiceOver Practice.
![]() Practice tapping, double-tapping, triple-tapping, and swiping.
Practice tapping, double-tapping, triple-tapping, and swiping.
![]() Tap Done to select the button, and then double-tap Done.
Tap Done to select the button, and then double-tap Done.
![]() On the VoiceOver screen, tap Speaking Rate to select it, and then swipe up or down to adjust the rate. Swiping up or down is the VoiceOver gesture for adjusting the slider.
On the VoiceOver screen, tap Speaking Rate to select it, and then swipe up or down to adjust the rate. Swiping up or down is the VoiceOver gesture for adjusting the slider.

![]() Swipe up with three fingers.
Swipe up with three fingers.
The screen scrolls down.
![]() Tap and then double-tap Speech and choose voice, pronunciations, and pitch options on the Speech screen.
Tap and then double-tap Speech and choose voice, pronunciations, and pitch options on the Speech screen.
![]() Tap and then double-tap Verbosity and choose which items to have VoiceOver announce.
Tap and then double-tap Verbosity and choose which items to have VoiceOver announce.
![]() Set the Always Speak Notifications switch to On (
Set the Always Speak Notifications switch to On (![]() ) or Off (
) or Off (![]() ), as needed.
), as needed.
![]() Tap and then double-tap Double-tap Timeout and set the timeout for double-tapping.
Tap and then double-tap Double-tap Timeout and set the timeout for double-tapping.
![]() Tap and then double-tap Typing Feedback.
Tap and then double-tap Typing Feedback.

The Typing Feedback screen appears.
![]() In the Software Keyboards area, tap and then double-tap the feedback type you want: Nothing, Characters, Words, or Characters and Words.
In the Software Keyboards area, tap and then double-tap the feedback type you want: Nothing, Characters, Words, or Characters and Words.
![]() In the Hardware Keyboards area, tap and then double-tap the feedback type you want: Nothing, Characters, Words, or Characters and Words.
In the Hardware Keyboards area, tap and then double-tap the feedback type you want: Nothing, Characters, Words, or Characters and Words.
![]() Tap and then double-tap VoiceOver (
Tap and then double-tap VoiceOver (![]() ).
).
The VoiceOver screen appears again.
Configure Other Accessibility Features
To help you see the screen better, iOS provides a full-featured zoom capability. After turning on zooming, you can display the Zoom Controller to give yourself easy control of zoom, choose the zoom region, and set the maximum zoom level.
The Follow Focus feature makes the zoomed area follow the focus on-screen. The Smart Typing feature makes iOS switch to Window Zoom when the keyboard appears, so that text is zoomed but the keyboard is regular size.
Configure Other Accessibility Features

Display the Accessibility Screen and Configure Zoom Settings
![]() Press Home.
Press Home.
The Home screen appears.
![]() Tap Settings (
Tap Settings (![]() ).
).
The Settings screen appears.
![]() Tap General (
Tap General (![]() ).
).
The General screen appears.
![]() Tap Accessibility.
Tap Accessibility.
The Accessibility screen appears.
![]() Tap Zoom.
Tap Zoom.

The Zoom screen appears.
![]() Set the Zoom switch to On (
Set the Zoom switch to On (![]() ).
).
![]() The Zoom window appears if the Zoom Region is set to Window Zoom.
The Zoom window appears if the Zoom Region is set to Window Zoom.
![]() Set the Follow Focus switch to On (
Set the Follow Focus switch to On (![]() ) or Off (
) or Off (![]() ).
).
![]() Set the Smart Typing switch to On (
Set the Smart Typing switch to On (![]() ) or Off (
) or Off (![]() ).
).
![]() Set the Show Controller switch to On (
Set the Show Controller switch to On (![]() ).
).
![]() The Zoom Controller appears.
The Zoom Controller appears.
![]() Drag the Maximum Zoom Level slider to set the maximum zoom level.
Drag the Maximum Zoom Level slider to set the maximum zoom level.
![]() Tap Idle Visibility.
Tap Idle Visibility.
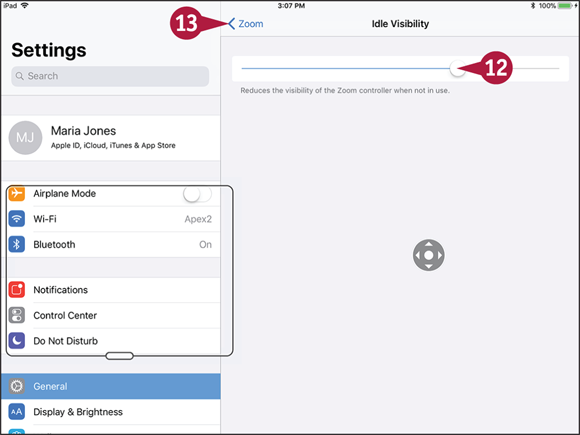
The Idle Visibility screen appears.
![]() Drag the slider to set the visibility percentage for the Zoom Controller when it is idle.
Drag the slider to set the visibility percentage for the Zoom Controller when it is idle.
Note: Move the slider on the Idle Visibility screen to the left to make the controller fade more after you have not used it for a while.
![]() Tap Zoom (
Tap Zoom (![]() ).
).
The Zoom screen appears again.
![]() Tap Zoom Region.
Tap Zoom Region.

The Zoom Region screen appears.
![]() Tap Full Screen Zoom or Window Zoom, as needed.
Tap Full Screen Zoom or Window Zoom, as needed.
Note: Window Zoom displays a movable window frame that you can position over the area you want to zoom, leaving the rest of the screen unchanged.
![]() Tap Zoom (
Tap Zoom (![]() ).
).
The Zoom screen appears again.
![]() Tap Zoom Filter.
Tap Zoom Filter.
The Zoom Filter screen appears.
![]() Tap the zoom filter you need: None, Inverted, Grayscale, Grayscale Inverted, or Low Light.
Tap the zoom filter you need: None, Inverted, Grayscale, Grayscale Inverted, or Low Light.
![]() Tap Zoom (
Tap Zoom (![]() ).
).
The Zoom screen appears again.
![]() Tap Accessibility (
Tap Accessibility (![]() ).
).
Your iPad includes several “display accommodations” such as inverting the screen colors entirely, reducing the white point to lessen the intensity of bright colors, and applying color filters for grayscale or for the protanopia, deuteranopia, or tritanopia color blindnesses.
You can also set a larger text size, apply shading around text-only buttons, reduce the transparency of items, and darken colors.

Configure Display Accommodations
![]() On the Accessibility screen, tap Display Accommodations.
On the Accessibility screen, tap Display Accommodations.
The Display Accommodations screen appears.
![]() Tap Invert Colors and set the Smart Invert switch or the Classic Invert switch to On (
Tap Invert Colors and set the Smart Invert switch or the Classic Invert switch to On (![]() ) to invert colors, as in this example.
) to invert colors, as in this example.
Note: Inverting colors disables the Night Shift feature.
![]() Set the Reduce White Point switch to On (
Set the Reduce White Point switch to On (![]() ) if you want to reduce the intensity of bright colors.
) if you want to reduce the intensity of bright colors.
![]() Drag the slider to adjust the white point.
Drag the slider to adjust the white point.
![]() Tap Color Filters.
Tap Color Filters.

The Color Filters screen appears.
![]() The color chart displays colors using the filtering you apply. Swipe left to see other color samples.
The color chart displays colors using the filtering you apply. Swipe left to see other color samples.
![]() Set the Color Filters switch to On (
Set the Color Filters switch to On (![]() ).
).
The list of color filters appears.
![]() Tap the filter you want to apply: Grayscale, Red/Green Filter, Green/Red Filter, Blue/Yellow Filter, or Color Tint.
Tap the filter you want to apply: Grayscale, Red/Green Filter, Green/Red Filter, Blue/Yellow Filter, or Color Tint.
![]() If the Intensity slider appears, drag it to adjust the intensity.
If the Intensity slider appears, drag it to adjust the intensity.
![]() For Color Tint, drag the Hue slider to adjust the hue.
For Color Tint, drag the Hue slider to adjust the hue.
![]() Tap Display Accommodations (
Tap Display Accommodations (![]() ).
).
![]() Tap Accessibility (
Tap Accessibility (![]() ).
).
The Accessibility screen appears again.

Configure Visual Interface Accessibility Settings
![]() On the Accessibility screen, you can set the Bold Text switch to On (
On the Accessibility screen, you can set the Bold Text switch to On (![]() ) to make text appear bold. You must restart your iPad to effect this change.
) to make text appear bold. You must restart your iPad to effect this change.
![]() You can set the Button Shapes switch to On (
You can set the Button Shapes switch to On (![]() ) to make shapes appear around text buttons, as on the General button here.
) to make shapes appear around text buttons, as on the General button here.
![]() You can set the On/Off Labels switch to On (
You can set the On/Off Labels switch to On (![]() ) to display I and O labels on the switches, as shown here.
) to display I and O labels on the switches, as shown here.
![]() Tap Larger Text.
Tap Larger Text.

The Larger Text screen appears.
![]() Set the Larger Accessibility Sizes switch to On (
Set the Larger Accessibility Sizes switch to On (![]() changes to
changes to ![]() ).
).
![]() Drag the slider to set the text size.
Drag the slider to set the text size.
![]() Tap Accessibility (
Tap Accessibility (![]() ).
).
The Accessibility screen appears again.
Your iPad includes a suite of interaction features designed to make it easier for you to interact with the touch screen and other hardware components, such as the accelerometers that detect and analyze the device’s movements. Changes you can make include setting the tap-and-hold duration, adjusting the repeat interval, and configuring the double- and triple-click speed for the Home button. You can also choose your default audio device for call audio.

Configure Interaction Accessibility Features
![]() On the Accessibility screen, tap Touch Accommodations.
On the Accessibility screen, tap Touch Accommodations.
The Touch Accommodations screen appears.
![]() Set the Touch Accommodations switch to On (
Set the Touch Accommodations switch to On (![]() ) to enable touch accommodations.
) to enable touch accommodations.
Note: If the Important dialog opens, warning you that Touch Accommodations changes iPad-control gestures, tap OK.
![]() Set the Hold Duration switch to On (
Set the Hold Duration switch to On (![]() ) if you need to adjust the hold duration.
) if you need to adjust the hold duration.
![]() Tap + or – to set the Hold Duration time.
Tap + or – to set the Hold Duration time.
![]() Set the Ignore Repeat switch to On (
Set the Ignore Repeat switch to On (![]() ) if your iPad detects false repeat touches.
) if your iPad detects false repeat touches.

![]() Tap + or – to set the Ignore Repeat interval.
Tap + or – to set the Ignore Repeat interval.
![]() In the Tap Assistance box, tap Off, Use Initial Touch Location, or Use Final Touch Location, as needed.
In the Tap Assistance box, tap Off, Use Initial Touch Location, or Use Final Touch Location, as needed.
![]() In the Tap Assistance Gesture Delay box, tap + or – to set the delay on tap assistance. This is the length of time you get to perform a tap; beyond this point, the iPad assumes you are making a gesture other than tapping.
In the Tap Assistance Gesture Delay box, tap + or – to set the delay on tap assistance. This is the length of time you get to perform a tap; beyond this point, the iPad assumes you are making a gesture other than tapping.
![]() Tap Accessibility (
Tap Accessibility (![]() ).
).

The Accessibility screen appears again.
![]() Tap Shake to Undo to display the Shake to Undo screen, set the Shake to Undo switch to Off (
Tap Shake to Undo to display the Shake to Undo screen, set the Shake to Undo switch to Off (![]() ) if the feature undoes actions by accident, and then tap Accessibility (
) if the feature undoes actions by accident, and then tap Accessibility (![]() ) to return to the Accessibility screen.
) to return to the Accessibility screen.
![]() Tap Call Audio Routing to display the Call Audio Routing screen, tap the audio output device to use for FaceTime audio calls, such as Bluetooth Headset; and then tap Accessibility (
Tap Call Audio Routing to display the Call Audio Routing screen, tap the audio output device to use for FaceTime audio calls, such as Bluetooth Headset; and then tap Accessibility (![]() ) to return to the Accessibility screen.
) to return to the Accessibility screen.
![]() Tap Home Button.
Tap Home Button.

The Home Button screen appears.
![]() Tap Default, Slow, or Slowest to set the double-click speed.
Tap Default, Slow, or Slowest to set the double-click speed.
![]() In the Press and Hold to Speak section, tap Siri or Off, as needed.
In the Press and Hold to Speak section, tap Siri or Off, as needed.
![]() Set the Rest Finger to Open switch to On (
Set the Rest Finger to Open switch to On (![]() ) if you want to be able to unlock the iPad using Touch ID by resting your finger on the Home button without having to press the Home button.
) if you want to be able to unlock the iPad using Touch ID by resting your finger on the Home button without having to press the Home button.
![]() Tap Accessibility (
Tap Accessibility (![]() ).
).
The Accessibility screen appears again.
Using a Hardware Keyboard
Your iPad includes several on-screen keyboards that appear automatically when you tap a text field on the screen. You can switch among the keyboards as necessary to type the characters you need, and you can undock the keyboard or split it so that you can type easily with two thumbs while holding the iPad.
If you need to type extensively, you may prefer to connect a hardware keyboard to your iPad. This section details your options for a hardware keyboard, explains how to connect it, and shows you how to use it.
Choose a Hardware Keyboard

You can connect a keyboard to any iPad by using Bluetooth, which is usually effective and convenient for most purposes. For the iPad Pro, you can get one of Apple’s Smart Keyboard models, which connect via the custom Smart Connector on the iPad Pro models.
Many types of Bluetooth keyboards work well with iPads, but it is a good idea to verify the compatibility of any particular model before buying it. Keyboards designed specifically for the iPad, or for iOS devices in general, often include dedicated keys for functions such as displaying the Home screen, controlling the volume, and launching apps.

One option is to get a keyboard case designed specifically for the iPad model you have. This approach works well if you do not already have an iPad case, it is convenient for you to keep the iPad in the keyboard case, and you do not plan to switch iPad models in the near future. Some keyboard cases fully enclose the iPad, whereas others act as a protective cover for the screen but leave the iPad’s back exposed.
For more flexibility, you can get a Bluetooth keyboard designed for use with iOS but not customized for any particular device. You can then use the keyboard with any iOS device.
For the greatest flexibility, you can use any Bluetooth keyboard that is compatible with iOS; this includes Apple’s wireless keyboards for the Mac. For example, if you already have a Bluetooth keyboard, you may want to see if it works with your iPad. A Bluetooth keyboard can be active with only one device at a time.
Connect the Keyboard to the iPad

Once you have gotten your keyboard, connect it to your iPad. This section assumes you are using Bluetooth.
Unlock the iPad, press Home to display the Home screen, and then tap Settings (![]() ) to display the Settings screen. Tap Bluetooth (
) to display the Settings screen. Tap Bluetooth (![]() ) to display the Bluetooth screen, and set the Bluetooth switch to On (
) to display the Bluetooth screen, and set the Bluetooth switch to On (![]() ).
).
Turn the keyboard on, and then put the keyboard into pairing mode. How you do this depends on the keyboard, so you may need to read its documentation, but it often involves either pressing a dedicated pairing button or pressing and holding the power button until lights begin flashing in a particular pattern.
Tap the keyboard’s button in the Devices list on the Bluetooth screen in Settings. The Bluetooth Pairing Request dialog opens, showing a pairing code. Type this code on the keyboard and press ![]() or
or ![]() to authenticate the connection.
to authenticate the connection.
Configure the Keyboard

After connecting the keyboard, you can simply type on it after tapping a text field on the screen. But you can also change the keyboard layout if necessary.
To change the keyboard layout, press Home to display the Home screen, and then tap Settings (![]() ) to display the Settings screen. Tap General (
) to display the Settings screen. Tap General (![]() ) to display the General screen, and then tap Keyboard to display the Keyboards screen. Tap Hardware Keyboard at the top of the screen to display the Hardware Keyboard screen, and then tap the language you are using, such as English. On the screen that appears, such as the English screen, tap the layout you want, such as Dvorak or U.S. International – PC.
) to display the General screen, and then tap Keyboard to display the Keyboards screen. Tap Hardware Keyboard at the top of the screen to display the Hardware Keyboard screen, and then tap the language you are using, such as English. On the screen that appears, such as the English screen, tap the layout you want, such as Dvorak or U.S. International – PC.
Using Your iPad with Your Mac
If you have a Mac, you can enjoy the impressive integration that Apple has built into iOS and the Mac’s operating system, which is now called macOS but was formerly called OS X. Apple calls this integration Continuity. Continuity involves several features including Handoff, which enables you to pick up your work or play seamlessly on one device exactly where you have left it on another device. For example, you can start writing an e-mail message on your Mac and then complete it on your iPad.
To use Continuity, your iPad must be running iOS 8, iOS 9, iOS 10, iOS 11, or a later version. Your Mac must be running Yosemite, El Capitan, Sierra, High Sierra, or a later version. Your Mac must have Bluetooth 4.0 hardware. In practice, this means a Mac mini or MacBook Air from 2011 or later, a MacBook Pro or iMac from 2012 or later, a MacBook from 2014 or later, or a Mac Pro from 2013 or later.
Enable Handoff on Your iPad

To enable your iPad to communicate with your Mac, you need to enable the Handoff feature. Press the Home button to display the Home screen, tap Settings (![]() ) to open the Settings app, and then tap General (
) to open the Settings app, and then tap General (![]() ) to display the General screen. Tap Handoff to display the Handoff screen, and then set the Handoff switch to On (
) to display the General screen. Tap Handoff to display the Handoff screen, and then set the Handoff switch to On (![]() ).
).
Enable Handoff on Your Mac

You also need to enable Handoff on your Mac. To do so, click Apple (![]() ) on the menu bar and then click System Preferences to open the System Preferences window. Click General to display the General pane. Click Allow Handoff between this Mac and your iCloud devices (
) on the menu bar and then click System Preferences to open the System Preferences window. Click General to display the General pane. Click Allow Handoff between this Mac and your iCloud devices (![]() changes to
changes to ![]() ). You can then click System Preferences on the menu bar and click Quit System Preferences to quit System Preferences.
). You can then click System Preferences on the menu bar and click Quit System Preferences to quit System Preferences.
Work on the Same Task on Your Mac and Your iOS Devices

With Handoff enabled, you can easily start a task on one device, pick it up on another device, and finish it on a third. For example, you can start writing an e-mail message on your Mac at home, continue it on your iPhone as you commute, and then finish it on your iPad while waiting for a meeting to start. To perform a handoff, you click or tap the icon that appears on the Dock when a Handoff-compatible app is in use on another device.
Send and Receive Text Messages from Your Mac

Your Mac can already send and receive messages via Apple’s iMessage service, but when your cellular iPad’s Internet connection is available, your Mac can send and receive Short Message Service (SMS) and Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) messages directly through the iPad. This capability enables you to manage your messaging smoothly and tightly from your Mac.
Get Your Mac Online with Personal Hotspot

With Continuity, you can use your cellular iPad as a hotspot for your Mac without having to set up the Portable Hotspot feature. Click Wi-Fi (![]() ) on the menu bar on your Mac and then click your iPad’s entry on the pop-up menu to connect. The iPad’s menu entry on the Wi-Fi pop-up menu shows the signal strength and battery life, enabling you to make sure you don’t run your iPad down unusably low.
) on the menu bar on your Mac and then click your iPad’s entry on the pop-up menu to connect. The iPad’s menu entry on the Wi-Fi pop-up menu shows the signal strength and battery life, enabling you to make sure you don’t run your iPad down unusably low.
