
How it works
Sensory marketing is most obviously
used by the food and drinks
industries, but its use extends
to diverse products and services:
computers designed with tactile
materials, hotels scented to relax
customers, and even fireworks
displays featuring edible confetti.
Typical channels for sensory
marketing include field marketing
(in-store events, samples, and
person-to-person sales), direct mail,
and product delivery. For online
businesses, however, finding a
way to use it remains a challenge.
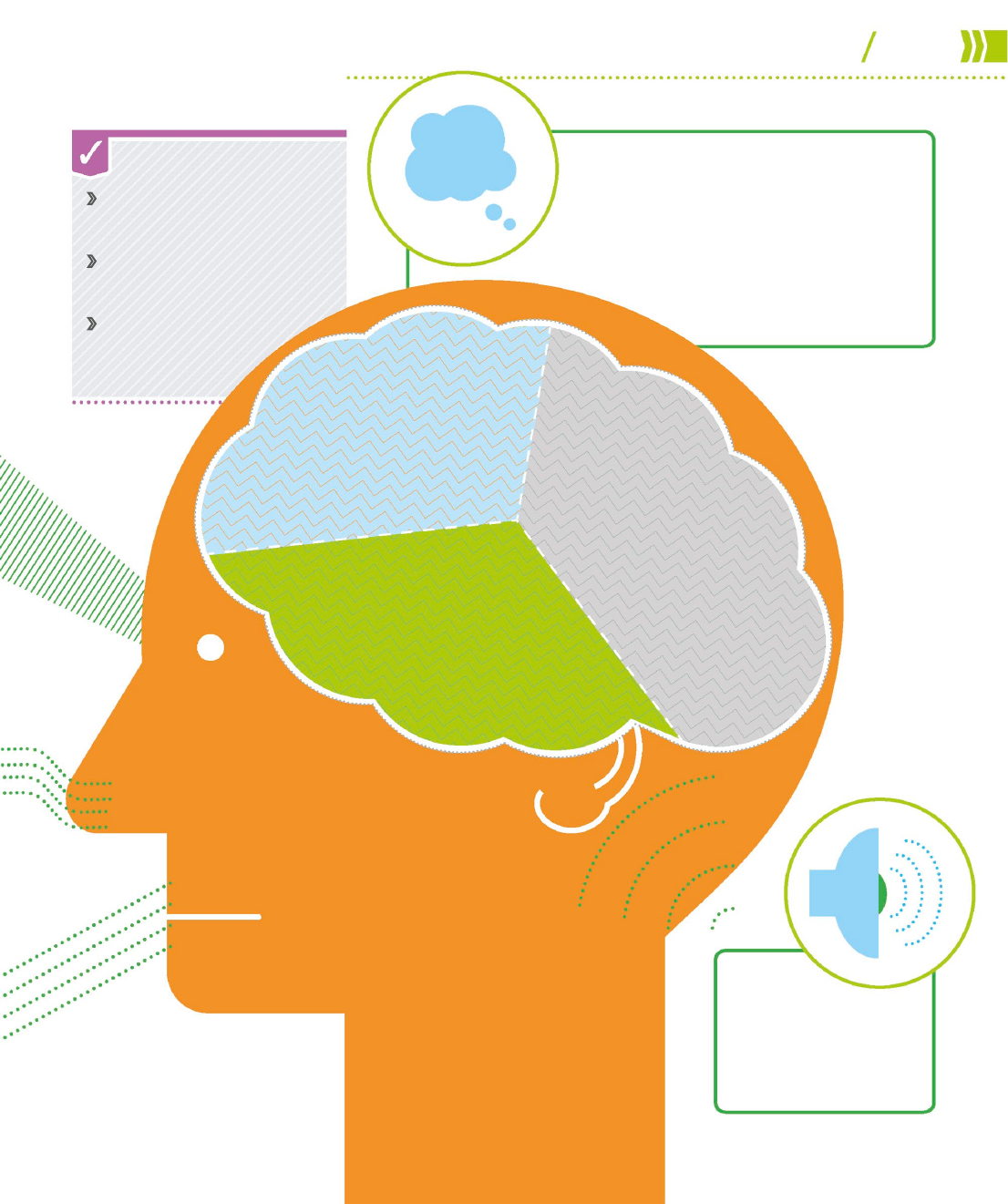
Sensory marketing
Sensory marketing targets multiple senses to sway purchasing
decisions. Based on research showing how the brain responds to
sensory input, this type of marketing acts covertly on the customer.
Sight
Technology is making advances
with this, the most stimulated
sense in marketing, by using
optical illusions, digital effects,
3-D, and 360-degree photography.
Touch
Marketers use 2-D and 3-D
textural print techniques for
promotional materials and
packaging, as well as to sell
products with tactile appeal.
Smell
Customers are willing to
pay more for a product
sold in an environment
that is scented appealingly.
Taste
Taste sensations
can be enhanced
or subtly altered by
combining them with
touch, sight, and especially the
closely linked sense of smell.
81%
of consumers
born from 1980
to 2000 value
experience over
material items
US_206-207_Sensory_Marketing.indd 206 21/11/2014 16:39
206 207
Sensory testing Assessment of
products by panel members with
exceptional sensory perception
Haptic technology Invention
that simulates touch through
vibrations on computers
3-D marketing
An immersive form of
consumer marketing
NEED TO KNOW
how sales and marketing works
Marketing approaches
Attitude, memory,
behavior, and mood
The sensory input results in a short- or long-
term effect on attitude, memory, behavior,
and mood. This can be influenced by the
intensity of sensory data and by using it to
stimulate more than one sense at the
same time.
Hearing
Sound is more
effective than sight
in triggering the
brain areas that
process emotions.
Perception
The brain receives
stimuli from one
or more senses.
Cognition
After processing
sensory stimuli, the brain
embeds memory,
regulates emotion, and
makes decisions.
Emotion
Sensory stimuli tap
into the store of
emotional memories, as
both are processed by the
same area of the brain.
US_206-207_Sensory_Marketing.indd 207 21/11/2014 16:39
206 207
Sensory testing Assessment of
products by panel members with
exceptional sensory perception
Haptic technology Invention
that simulates touch through
vibrations on computers
3-D marketing
An immersive form of
consumer marketing
NEED TO KNOW
how sales and marketing works
Marketing approaches
Attitude, memory,
behavior, and mood
The sensory input results in a short- or long-
term effect on attitude, memory, behavior,
and mood. This can be influenced by the
intensity of sensory data and by using it to
stimulate more than one sense at the
same time.
Hearing
Sound is more
effective than sight
in triggering the
brain areas that
process emotions.
Perception
The brain receives
stimuli from one
or more senses.
Cognition
After processing
sensory stimuli, the brain
embeds memory,
regulates emotion, and
makes decisions.
Emotion
Sensory stimuli tap
into the store of
emotional memories, as
both are processed by the
same area of the brain.
US_206-207_Sensory_Marketing.indd 207 21/11/2014 16:39

Starbucks
CASE STUDY
The strategy of coffee-shop chain
Starbucks exemplifies effective
relationship marketing. Centered on
core customer and internal markets,
it also involves suppliers, referrals,
and recruitment (employee) markets.
Marketing to customers
Social media
Business crowdsourcing
Familiarity with customers
Loyalty program
Reward card app
Mobile payments
Marketing internally
Barista training
Tech development opportunities
Marketing via referrals
Word of mouth
Social media shares
Marketing to employees
Stock options
Medical insurance
Partnership
Marketing to suppliers
Fairtrade programs
Quality control
How it works
Relationship marketing aims to
replicate the type of interaction
that village stores once had with
their customers, offering a high
level of personalized service
to win them over for a lifetime.
While small, local businesses
naturally work this way, large
Relationship
marketing
corporations have now changed
their focus from making the
sale to relationships, and from
short-term reward to long-term
gain. The marketer can extend
the network beyond the engaged
customer to include employees,
suppliers, and others.
Supplier markets
Building a relationship
of collaboration with
suppliers makes good
commercial sense.
Influence markets
To maintain good public
relations, the company works
with regulators and consumer
or environmental groups.
Six markets model
Relationship marketing has established a strategy for communicating with the
customer. This strategy defines six markets—not just traditional customer
markets—where companies should direct their marketing efforts.
The strategy of relationship marketing is to develop and
manage a trusting, long-term association with customers
and other markets that have links with the company.
US_208-209_Relationship_Marketing.indd 208 02/12/2014 14:58
208 209
how sales and marketing works
Marketing approaches
Customer markets
The main marketing focus is on
customers, but activities are based
more on building long-term
customer relationships than
on acquiring new customers.
Internal markets
A company’s employees are its
internal customers, working
together to represent its goals,
mission, and strategy.
Referral markets
Customers can be word-of-
mouth advocates for a company.
Related businesses may also
refer trade.
Recruitment markets
To attract the best
employees, a company may
market itself by offering
incentives to staff.
“Ignore the human
element of marketing
at your own peril.”
Bob Garfield
Key account management (KAM) System
that coordinates departments in a business-
to-business (B2B) company to serve big clients
Frequency marketing Promotion aimed
at increasing repeat sales by rewarding
customers for repeat purchases
Direct response (DR) Marketing that
invites consumers to respond directly to
the advertiser, by mail, telephone, or email
Transaction marketing Strategy that aims
to persuade customers to make additional
one-time purchases at the point of sale
NEED TO KNOW
CV
CV
CV
US_208-209_Relationship_Marketing.indd 209 21/11/2014 16:26

208 209
how sales and marketing works
Marketing approaches
Customer markets
The main marketing focus is on
customers, but activities are based
more on building long-term
customer relationships than
on acquiring new customers.
Internal markets
A company’s employees are its
internal customers, working
together to represent its goals,
mission, and strategy.
Referral markets
Customers can be word-of-
mouth advocates for a company.
Related businesses may also
refer trade.
Recruitment markets
To attract the best
employees, a company may
market itself by offering
incentives to staff.
“Ignore the human
element of marketing
at your own peril.”
Bob Garfield
Key account management (KAM) System
that coordinates departments in a business-
to-business (B2B) company to serve big clients
Frequency marketing Promotion aimed
at increasing repeat sales by rewarding
customers for repeat purchases
Direct response (DR) Marketing that
invites consumers to respond directly to
the advertiser, by mail, telephone, or email
Transaction marketing Strategy that aims
to persuade customers to make additional
one-time purchases at the point of sale
NEED TO KNOW
CV
CV
CV
US_208-209_Relationship_Marketing.indd 209 21/11/2014 16:26
..................Content has been hidden....................
You can't read the all page of ebook, please click here login for view all page.
