
274 275
How operations and production work
Manufacturing and production
De-pan and cool rolls
The rolls are removed from
their pans.
Bag up to complete
All the rolls finish the production
process together.
12
million
loaves of bread were
sold every day in the
UK, in 2014
De-pan and cool bread
The large brown loaves are removed
from their pans.
Slice and bag
loaves
The loaves
are sliced and
packed for sale.
Pros
Economies of scale: low unit
costs, as large number is made
Customer offered choice
of, for example, size, weight,
and flavor
Output and productivity
increases with use of specialty/
dedicated machinery
Cons
Repetitive work, so workers
may be less motivated
Costly because may require
storage of raw materials, work
in progress, and finished items
(see p.139)
Requires detailed planning
and scheduling
BATCH PRODUCTION PROS AND CONS
Bake rolls
The whole batch is
baked at the same
time at the same
temperature.
Bake loaves
Baking time is longer
than for Batch 1, as
the units are larger.
US_274-275_Batch_Production.indd 275 21/11/2014 16:28

Chassis assembly Wheel assembly Engine assembly
Main body assembly
Windshield
assembly
Electrical
assembly
Car assembly
Parts assembly
How it works
Flow production typically involves large factories
equipped with conveyor belts and expensive
machinery, the assembly of individual components,
which may be bought in from other companies, and
the automation of tasks. Car manufacturing is an
example where elements of the car are put together
along a line; robot arms may install wheels and
workers may perform specialized jobs. Significant
output is possible with even a small number of
workers. Newspaper printers, oil refineries, and
chemical plants also use flow production.
The purpose of flow (mass) production is to produce a large number
of identical, standardized items. This usually happens on a moving
line, which can be interrupted when the product is changed.
Flow production
The production line
In flow production, the item being made, such as a car, moves on a conveyor belt through different
stages until completion. Components to build the car may have been outsourced or produced in
another of the company’s factories. They are all ready to be used along the line.
US_276-277_Flow_Production.indd 276 21/11/2014 16:28
276 277
Inspection
FinishingDoor assembly
Gear box assembly Radiator assembly Seat assembly
how operations and production work
Manufacturing and production
60
million
cars are produced
globally each year
Pros
Economies of scale: can produce
large number of goods cheaply
Unskilled labor keeps costs low
Materials bought in large quantities,
so low cost
Cons
Expensive machinery requires
significant investment
Repetitive work means workers may
be less motivated
Reliant on equipment: if line breaks,
production is halted
FLOW PRODUCTION PROS AND CONS
Ready for
customer
When customer
demand is high,
car companies
may run their
production lines
continuously.
US_276-277_Flow_Production.indd 277 21/11/2014 16:28

276 277
Inspection
FinishingDoor assembly
Gear box assembly Radiator assembly Seat assembly
how operations and production work
Manufacturing and production
60
million
cars are produced
globally each year
Pros
Economies of scale: can produce
large number of goods cheaply
Unskilled labor keeps costs low
Materials bought in large quantities,
so low cost
Cons
Expensive machinery requires
significant investment
Repetitive work means workers may
be less motivated
Reliant on equipment: if line breaks,
production is halted
FLOW PRODUCTION PROS AND CONS
Ready for
customer
When customer
demand is high,
car companies
may run their
production lines
continuously.
US_276-277_Flow_Production.indd 277 21/11/2014 16:28
How it works
Mass customization offers new
opportunities for the manufacturing
and service industries. Social
media, online technology, 3-D
modeling tools, e-commerce
software, and flexible production
systems and processes are
allowing customers to configure
products to match their own tastes
and needs. Industries such as
footwear (particularly athletic
shoes), clothing, cars, jewelry, and
Mass customization
computers already allow consumers
to customize their purchases. The
price is generally higher than for
standardized goods.
Revolutionary new technologies
are expected to further extend
customization, allowing individuals
to, for example, scan their body
contours and use augmented reality
to design and order unique clothing.
Customers design own products
Mass customization has enormous potential to change consumerism. For
example, consumers can buy shoes designed to their own specification
via the internet. This is a high-status commodity among certain groups.
Sophisticated technology and manufacturing developments allow mass
products to be personalized. The low unit costs of mass production
combine with the marketing opportunities of custom-made.
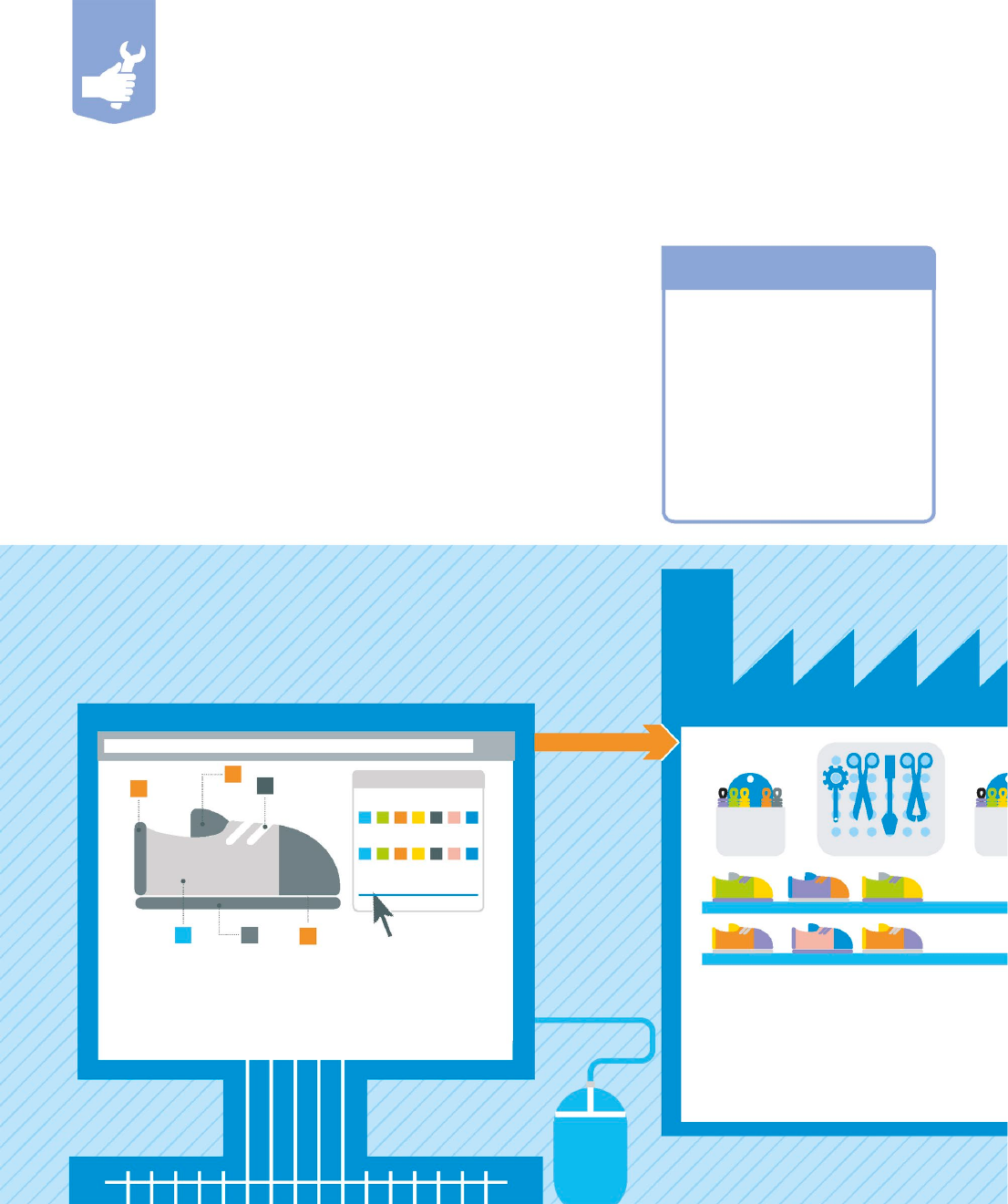
The customer decides
On the company’s website, a drop-down menu, with
options including style, shape, size, color, and laces,
allows consumers to design their own pair of shoes.
Sends order to factory
The firm holds no finished stock
but manufactures to order from
a range of parts, getting paid by
the customer before production.
Lace color
Shoe color
Name
FOOD MIXES
The generation raised on social
media expects to personalize every
aspect of their lives, and food and
drink is set to be a growth area
for mass customization. Websites
allow consumers to make their own
cereal mixes, which is especially
useful for those with allergies, and
to create their own blends of tea
and coffee.
Laces
Tools
US_278-279_Mass_Customization.indd 278 21/11/2014 16:28
278 279
How operations and production work
Manufacturing and production
FOUR TYPES OF MASS CUSTOMIZATION
Collaborative customization
Work with individual customer to
develop specific product to suit
their needs. Technology firm Dell,
for example, assembles computers
to customer’s specification.
Adaptive customization
Produce standardized products
that are customizable by end-user.
For instance, US company Lutron
produces a lighting system that
lets customers choose own setting
from programmed settings.
Transparent customization
Provide unique products to
individuals without overtly
stating items are customized:
the Ritz-Carlton hotel group
keeps a database of preferences
for pillows and newspapers to
personalize a guest’s stay.
Cosmetic customization Make
a standardized product but market
it differently: Hertz distinguishes
its standard rental car from its
#1 Club Gold program.
$10
million
the total value of
customized sweets
sold by Mars by
2007, including
coloured M&M’s
Shoes shipped to customer
The customer receives a differentiated
product and has the psychological benefit
of personal design—at a price.
In his book Mass Customization: The New Frontier in Business Competition,
B. Joseph Pine II outlines four distinct types:
Patterned laces
Cushioned sole
Size 7.5, narrow fit
US_278-279_Mass_Customization.indd 279 21/11/2014 16:28

278 279
How operations and production work
Manufacturing and production
FOUR TYPES OF MASS CUSTOMIZATION
Collaborative customization
Work with individual customer to
develop specific product to suit
their needs. Technology firm Dell,
for example, assembles computers
to customer’s specification.
Adaptive customization
Produce standardized products
that are customizable by end-user.
For instance, US company Lutron
produces a lighting system that
lets customers choose own setting
from programmed settings.
Transparent customization
Provide unique products to
individuals without overtly
stating items are customized:
the Ritz-Carlton hotel group
keeps a database of preferences
for pillows and newspapers to
personalize a guest’s stay.
Cosmetic customization Make
a standardized product but market
it differently: Hertz distinguishes
its standard rental car from its
#1 Club Gold program.
$10
million
the total value of
customized sweets
sold by Mars by
2007, including
coloured M&M’s
Shoes shipped to customer
The customer receives a differentiated
product and has the psychological benefit
of personal design—at a price.
In his book Mass Customization: The New Frontier in Business Competition,
B. Joseph Pine II outlines four distinct types:
Patterned laces
Cushioned sole
Size 7.5, narrow fit
US_278-279_Mass_Customization.indd 279 21/11/2014 16:28
..................Content has been hidden....................
You can't read the all page of ebook, please click here login for view all page.
